A headphone (also referred to as a headset or earphone) is an output audio device used to listen to sound privately by wearing it over or inside the ears. It connects to source devices such as computers, laptops, tablets, mobile phones, portable music players, CD players, electronic musical instruments, gaming consoles, or amplifiers.
It typically consist of a pair (stereo) — or sometimes a single (mono) — small loudspeakers with drivers that are worn on or around the head, covering or resting on the user’s ears. They are electroacoustic transducers that convert electrical signals into sound waves.
In today’s world, a good pair of headphones is more than just an accessory—it is an essential part of our daily lives. Whether you are listening to music on your commute, attending virtual meetings, gaming, or working in a studio, the right gear completely transforms how you experience sound.
However, with so many options available, choosing the right pair can feel like navigating a maze. From casual listeners to dedicated audiophiles, the endless variety of designs and technical terminology can be overwhelming.
But fear not!
This guide is designed to demystify the vast array of listening devices available today.
We’ll explore all the different types of headphones and earphones by fitting style, by enclosure design, by connection, by driver technology, by purposes, and by use cases. We also explain their unique features and help you determine which style best suits your lifestyle and listening preferences, along with a few notable mentions—without using any affiliate links.
Get ready to embark on a visual journey through the incredible world of personal audio!
Let’s get started.
Different Types of Headphones by Fitting Style (Size)
Headphones and earphones come in a variety of fitting styles and sizes, which determine how they sit on or in your ear and directly impact comfort, portability, noise isolation, and overall listening experience. Understanding these fitting styles will help you choose a design that best matches your lifestyle, usage habits, and personal comfort preferences. Fitting style also plays a key role in head and ear size compatibility—some designs are better suited for larger or smaller heads, different ear shapes, or users who wear glasses. Adjustable headbands, earcup depth, clamping force, and ear-tip sizes all contribute to how well a headphone fits and feels.
► Now, let’s explore the different types of headphones and earphones by fitting style and size, including:
1. Over-Ear Headphones

The history of headphones begins in the late 19th century, when the first version—a single earpiece that was worn on the user’s shoulder and weighed over 10 pounds—was developed to enable hands-free communication for telephone operators. Later, in the early 1900s, over-ear headphones were introduced, in which two ear cups were connected by a headband, laying the foundation for the modern headphone design we use today.
Over-ear headphones, also known as circumaural headphones, are designed with large ear cups that completely enclose the ears. The ear cushions form a seal around the ears, creating a comfortable fit that helps block out outside noise and improves sound immersion.
They are the most traditional and professional-looking headphones, often used by audiophiles, studio engineers, and gamers who value high-quality, detailed sound. Because they typically have larger drivers (typically 40mm to 60mm), they allow them to produce richer bass, clearer mids, and crisper highs that in-ear and on-ear headphones do not. Because of this, they offer a wider soundstage than over-ears do—meaning you can easily distinguish between instruments and directions in music or games.
Most over-ear headphones are closed-back, which prevents sound from escaping and blocks outside noise. However, there are also open-back designs that allow air and sound to pass through the ear cups, providing a more natural and spacious listening experience — ideal for studio mixing and critical listening. Alternatively, semi-open headphones offer a balanced sound for those who need versatility in different listening situations. And I have discussed about these in detail, which you will find below.
Overall, comfort is another big advantage. Padded ear cups and adjustable headbands make them suitable for long listening sessions with powerful sounds, whether you are editing audio, streaming, or relaxing at home. However, the trade-off is size and portability – over-ear headphones are heavier and less convenient to carry than in-ear and on-ear models.
2. On-Ear Headphones

On-ear headphones, also known as supra-aural headphones, are designed with ear pads that sit directly on top of the ear rather than covering the top of the ear like over-ear headphones. This design makes them lighter, more compact, and portable, making them attractive to users who want comfort without the bulk, especially for phone calls or conference calls.
Historically, it became popular in the 1980s, especially with the rise of portable cassette players like the Sony Walkman, which revolutionized personal listening. Their lightweight construction allowed people to enjoy music on the go – a major change from the bulky, studio-style over-ear designs of previous decades.
In terms of sound quality, on-ear headphones often deliver a vibrant and engaging sound signature, but because the ear cups rest on top of the ears rather than around them, they provide less passive noise isolation and a slightly bass-boosted sound. This means some external noise can still be heard — which can actually be beneficial in certain environments, such as offices or outdoor settings, where awareness of your surroundings is important. However, this design may not be ideal for those who prefer complete isolation or deep, immersive listening experiences.
Modern on-ear headphones come in both wired and wireless versions, often with Bluetooth connectivity, built-in microphones, and foldable designs for convenience. Many models also incorporate noise-canceling technology, although this is usually less effective than over-ear headphones due to the loose ear seal. Still, they are a great middle ground for those who find over-ear models too big or in-ear models uncomfortable.
3. Around-Ear Headphones

Around-ear headphones, also known as circumaural headphones, are designed with large, cushioned ear cups that completely surround the ear rather than sit on top of it. This design provides a secure and comfortable fit, excellent noise isolation, and a rich, immersive listening experience.
These headphones are a staple among audiophiles, studio professionals, and serious music lovers because they deliver deep bass, clear mids, and natural highs with a wide soundstage that feels like listening in a dedicated acoustic space.
4. Clip-On Headphones

Clip-on headphones, now better known as clip-on earbuds or a type of open-ear headphones but comes with different fitting style like on-ear headphones, are an alternative type of audio device with a unique fit.
Unlike traditional in-ear earbuds that go into your ear canal or over-ear headphones that cover your entire ear, clip-on headphones attach securely to the outer edge of your ear using a small, lightweight hook or clip mechanism.
The main difference is that clip-on headphones or earbuds use the ear’s structure (the pinna) for stability and an open fit. On the other hand, on-ear headphones use a headband to press the ear cups against the ear, while in-ear headphones use a tip inserted into the ear canal to create a sealed fit.
5. Convertible Headphones
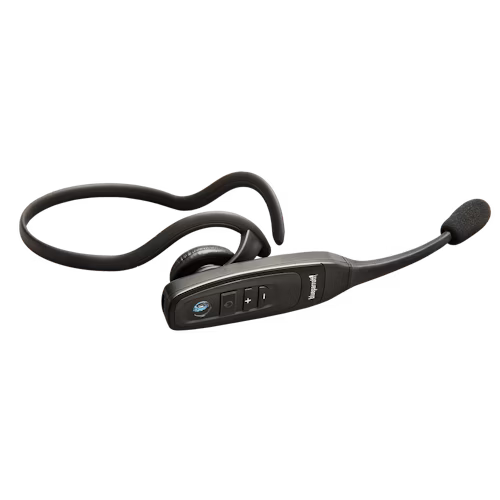

A convertible headphone or headset is an audio device that is designed to be worn in multiple different styles using interchangeable parts. Its main purpose is versatility, which allows the user to adapt the device to their current activity or environment without the need for a second product.
These headphones can be physically reconfigured into multiple wearing styles — such as a headband, ear hook, or neckband — using interchangeable parts, allowing the user to adapt the product to their environment or activity. This flexibility effectively transforms their fundamental design. A notable example is a single-ear mono headset that can be converted into a two-ear stereo headphone by attaching a separate ear cup or pad.
6. Bone Conduction Headphones
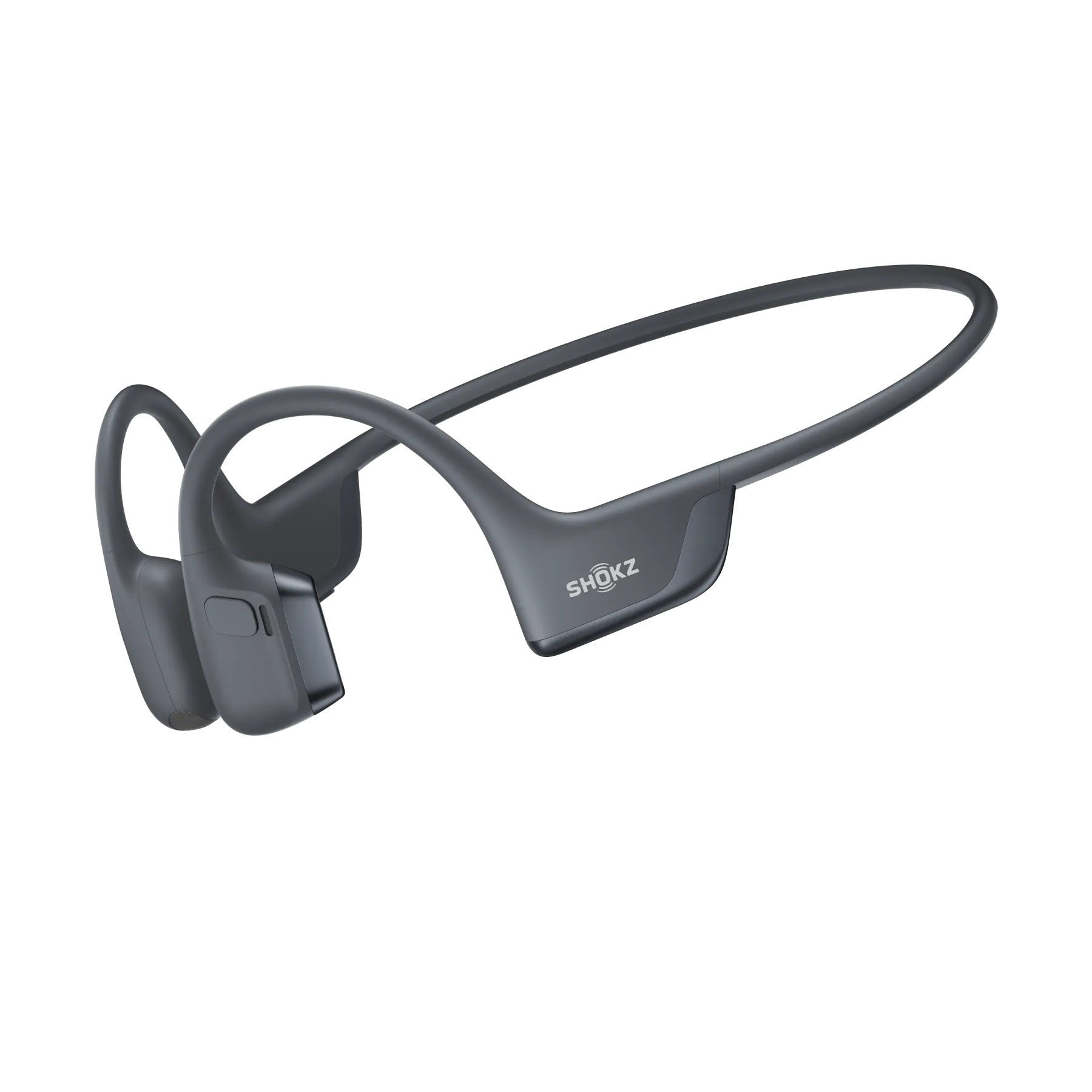

This means your ear canals remain open, allowing you to stay aware of your surroundings while still hearing your audio. Because of this open-ear design, there are popular among runners, cyclists, and outdoor enthusiasts, as well as individuals with certain types of hearing loss that affect the outer or middle ear.
They typically rest just in front of your ears, not on or inside them, and use piezoelectric transducers to create vibrations that you perceive as sound. While they don’t offer the same bass depth or sound isolation as traditional models, they provide a unique balance of safety, comfort, and situational awareness.
7. In-Ear Headphones or Earphones (In-ear monitors or IEMs)

In-ear headphones are small audio devices that insert a tip directly into the ear canal to achieve a secure, noise-isolating fit, a concept first patented in 1891 but popularized by musicians in the 1980s for improved stage monitoring. This segment currently dominates the headphone market, driven by the popularity of True Wireless (TWS) technology and key features such as improved noise isolation, with revenues expected to reach several billion dollars worldwide.
► ► Let’s explore the different types of in-ear headphones you can find right now, including:
7.1 Canalphones
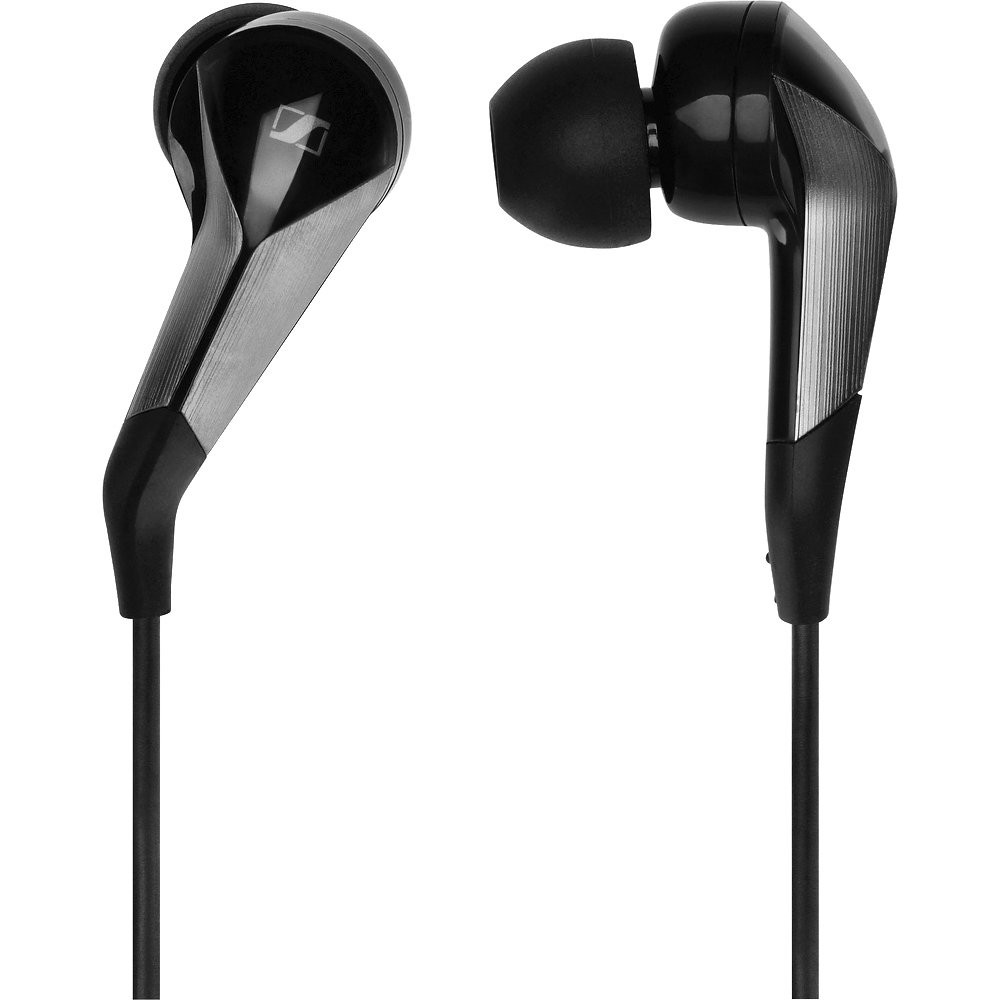

Canalphones are a term for in-ear headphones that are specifically designed to be inserted into and sealed within the ear canal using soft tips (silicone or foam). This is an important design feature that ensures superior passive noise isolation and optimal reproduction of deep bass frequencies.
The Sennheiser CX 870 is a classic example of a canalphone. It features a shallow-to-medium ear canal fit with a single dynamic driver, providing good comfort, decent passive isolation, and a clean, consumer-friendly sound.
Although the CX 870 is no longer in production, similar canalphone models are available today, including the Sony MDR‑EX155AP, Panasonic ErgoFit RP‑HJE120, JBL Tune 110, Philips SHE3590, Xiaomi Mi Earphones Basic, and Samsung AKG-tuned wired earphones. These options maintain the classic canalphone design while offering comfortable, lightweight listening for casual use.
7.2 In-Ear Monitors (IEMs)
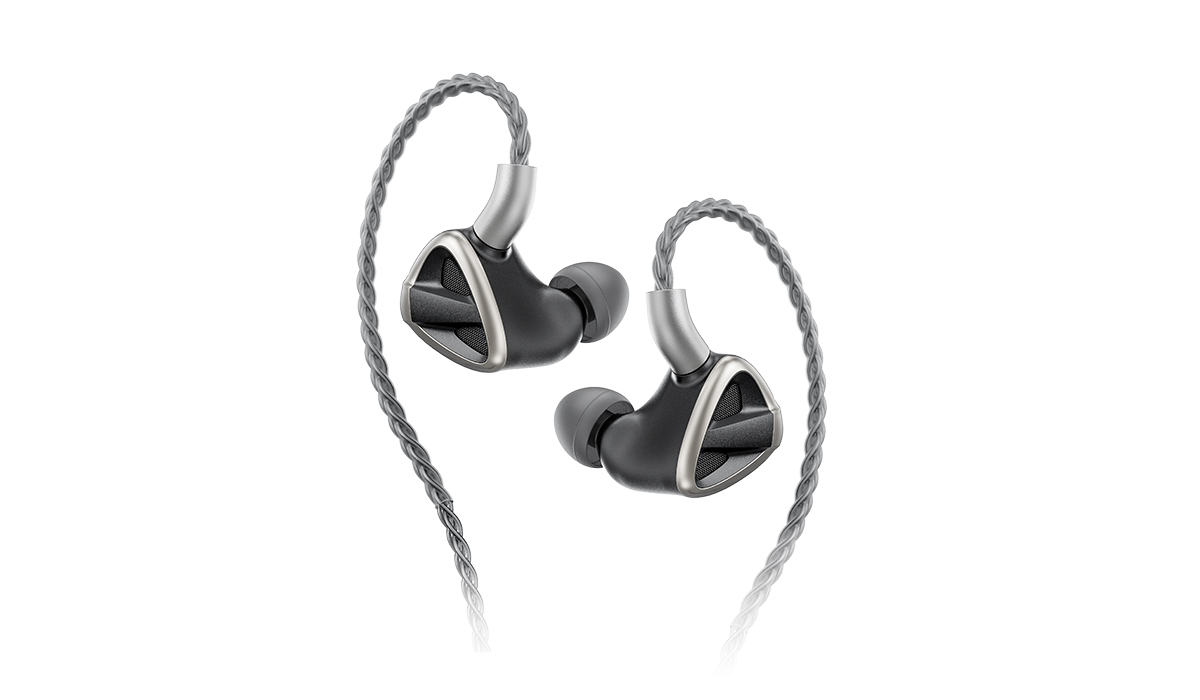

The main difference between In-Ear Headphones (the general category) and IEMs (In-Ear Monitors) is primarily one of intent, design quality, and purpose. For example, both sit inside the ear canal, but general in-ear headphones rest near the canal entrance for greater comfort and lighter isolation, while IEMs sit deeper in the canal, offering a more secure fit with higher isolation—though typically with slightly less comfort for some users.
In shorter, all IEMs are In-Ear Headphones, but not all In-Ear Headphones are IEMs. In-Ear Headphones is the broad category of any listening device that sits in or near the ear canal, ideal for general consumers. On the other hand, IEMs represent the high-fidelity, professional-grade subcategory focused on superior isolation, fit, and technical sound accuracy, ideal for professionals and audiophiles.
7.3 Earbuds

Earbuds are the most basic and traditional type of in-ear listening device. They sit outside the ear—specifically in the concha (the bowl-shaped part of the outer ear)—rather than going deep into the ear. Because they don’t create a tight seal, earbuds provide a lightweight and comfortable fit, making them easy to wear for long periods of time without pressure or fatigue.
However, this shallow fit provides minimal noise isolation. External noise can easily penetrate, and the low-frequency bass response is generally weaker than that of canal phones or IEMs that create a sealed fit. Still, many users prefer this “open” and comfortable listening experience, especially for casual listening at home, in the office, or while traveling. Some modern earbuds also feature active noise cancellation (ANC), which electronically reduces external noise—although the isolation is still not as strong as sealed in-ear designs.
Earbuds are often affordable, widely bundled with smartphones and music players, and easy to use. Classic models like the Apple EarPods and Bose Quitecomfort are popular for their comfort and familiarity, though they don’t match the isolation or audio accuracy of more in-ear headphones.
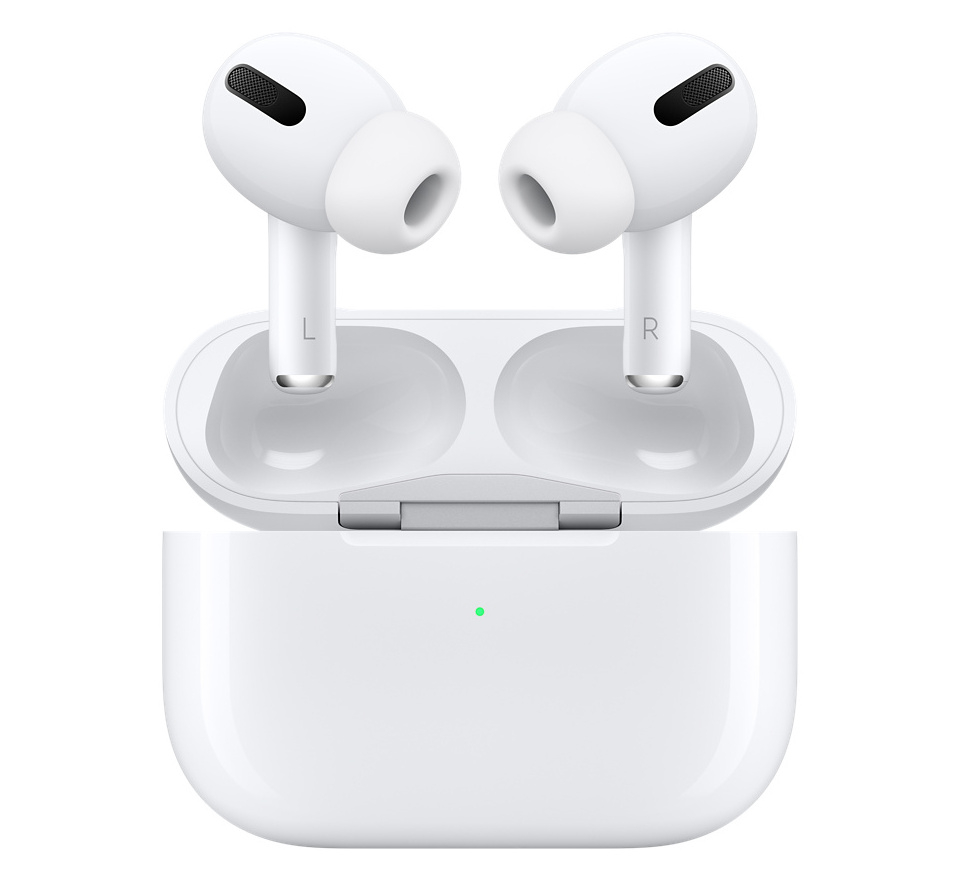
7.4 True Wireless Earbuds (TWS)
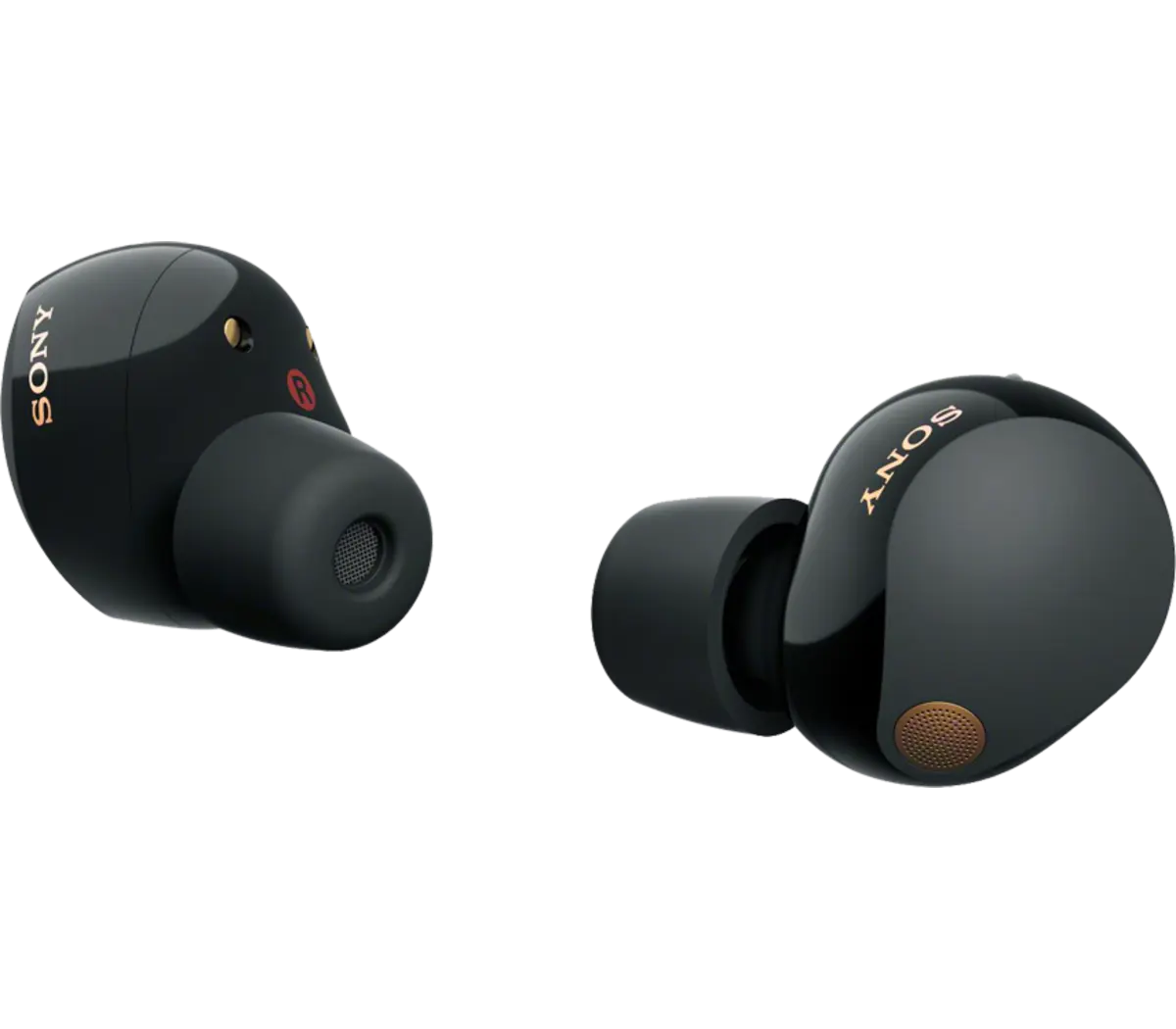

True Wireless Earbuds (TWS) are fully wireless earphones with no cables between the earpieces or to the audio source. Each earbud connects independently—usually via Bluetooth—and comes with a charging case that provides additional battery life and safe storage.
Because they seal the ear canal, most TWS models offer good passive noise isolation, and many include active noise cancellation (ANC), touch controls, transparency/ambient modes, and app-based customization. Their compact, cable-free design makes them ideal for daily use, commuting, workouts, and phone calls.
While both TWS and traditional earbuds are small in-ear style devices, they differ in key design and functional areas: TWS models offer better isolation, include advanced features like ANC, transparency modes, touch controls, app customization, and even high-resolution wireless codecs like LDAC on premium models such as the Sony WF-1000XM5.
They also operate completely wire-free with a charging case for portability. Traditional earbuds, on the other hand, rest outside the ear canal, offer minimal isolation, and typically lack modern smart features or high-quality wireless audio support, making them simpler but less versatile.
7.5 Wireless Neckband Headphones
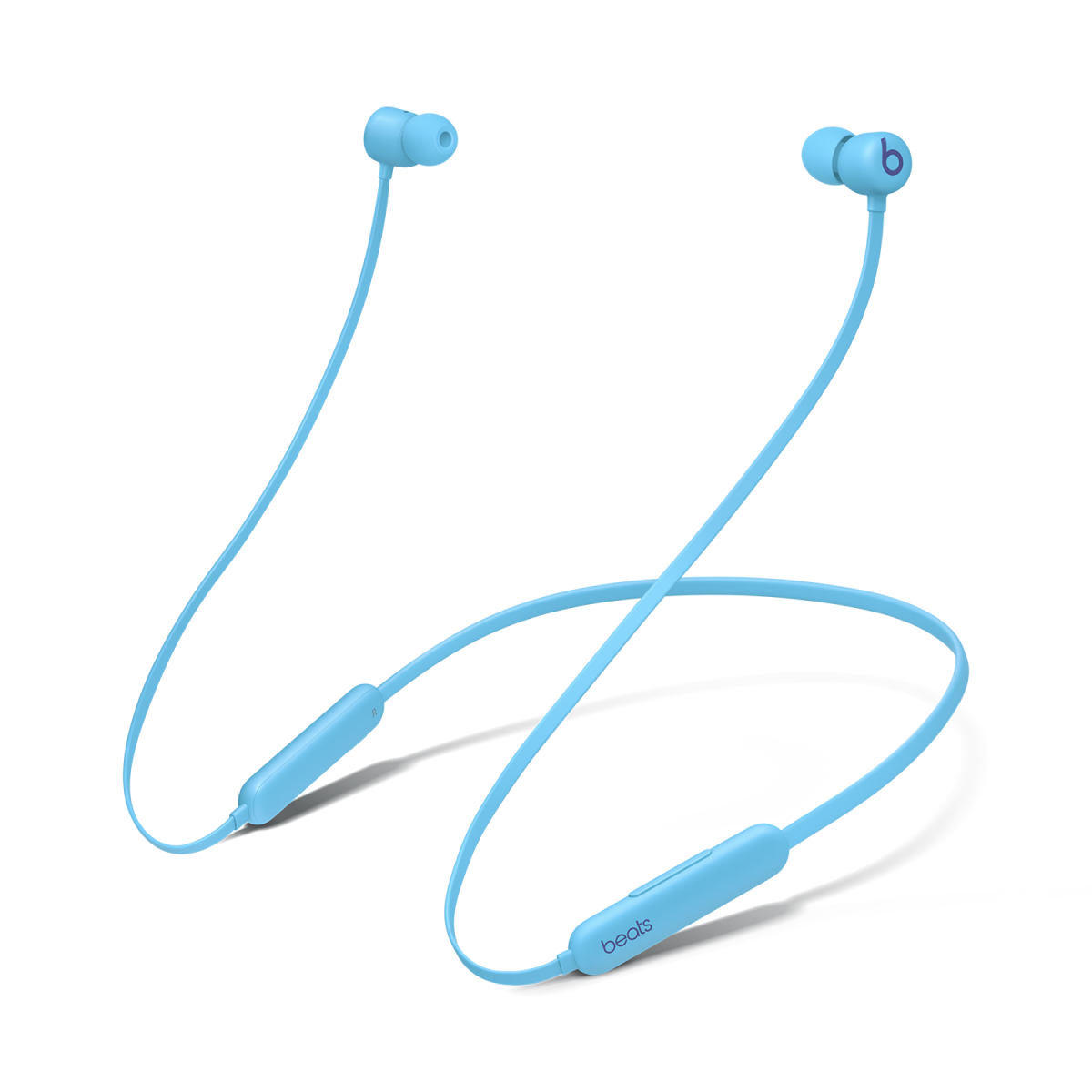

Wireless neckbands are in-ear earphones that are attached to the neck by a flexible band. Rather than being truly wireless like earbuds, these are connected to the neckband by a short wire, while the band itself houses the battery, Bluetooth module, microphone, and control buttons. This design offers a stable, lightweight fit that remains secure during movement, making neckbands particularly popular for commuting, office use, and workouts.
Because the neckband houses a larger battery, these models typically offer longer playback times than most TWS earbuds—often 10 to 20+ hours on a single charge. The wired connection to each earpiece also reduces the chance of audio dropouts and allows for easy magnetic “snap-together” storage when not in use.
When it comes to sound, these type of earbuds are generally balanced, tuned for everyday listening, though some models offer enhanced bass or support higher-quality Bluetooth codecs like AAC, aptX, or LDAC. Many also include vibration alerts, multi-point Bluetooth pairing, and inline controls for convenience.
Popular examples include the Beats Flex, Sony WI-C310, OnePlus Bullets Wireless Z2, Realme Buds wireless, and Samsung Level U2—providing reliable comfort, long battery life, and hassle-free wireless performance for those who prefer a connected yet lightweight design.
Different Types of Headphones by Enclosure Design
Enclosure design refers to how a headphone’s earcups are constructed and how sound is allowed to move in or out of them. This design plays a major role in shaping the listening experience, influencing soundstage, bass response, noise isolation, and sound leakage. Choosing the right enclosure type can significantly affect how immersive or private your listening feels, especially depending on whether you’re using your headphones at home, in the studio, or in public spaces.
► Now, let’s explore the different types of headphones by enclosure designs and understand how each one affects sound and usability, including:
8. Closed-Back Headphones
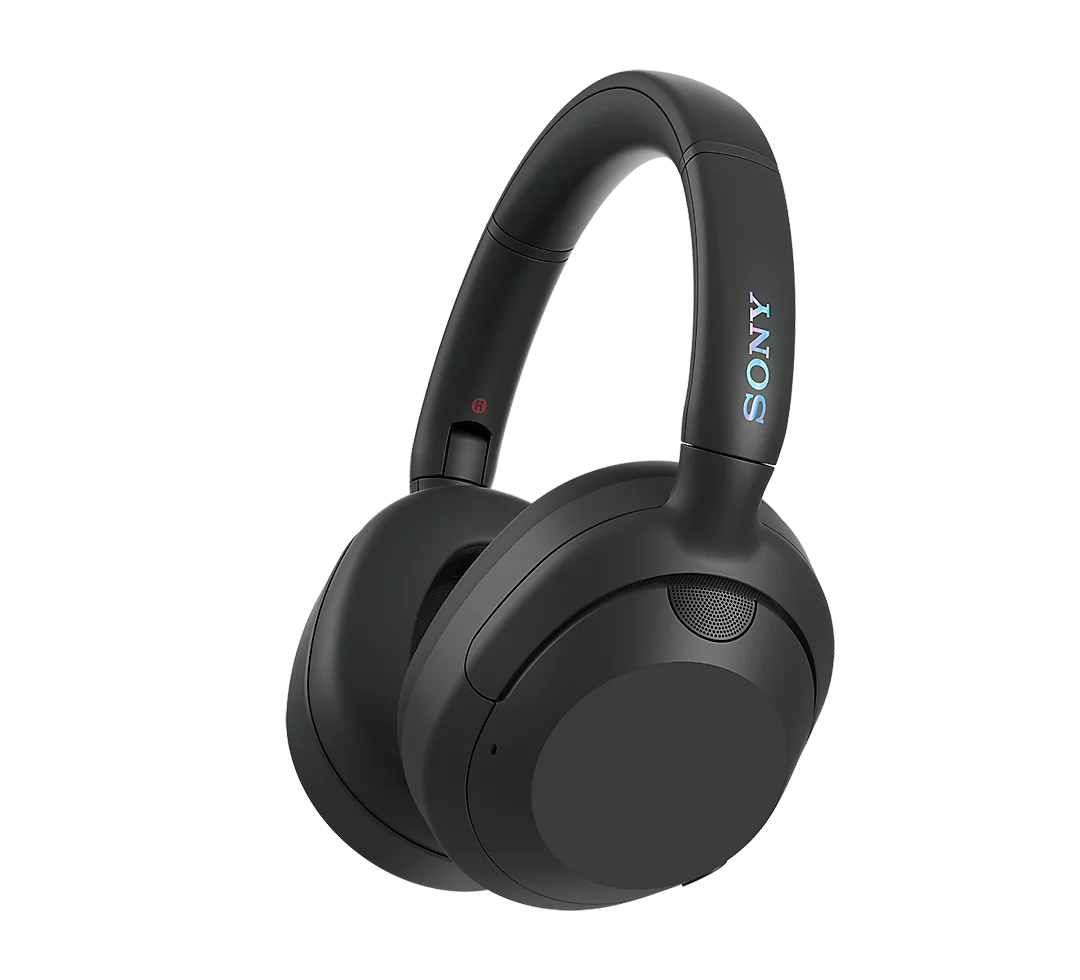

Closed-back headphones are designed with solid earcup enclosures that completely seal the back of the earcups, preventing sound from escaping and minimizing outside noise from entering. This design creates a more isolated listening experience, making them ideal for environments where external noise is a distraction or when you don’t want your audio to leak out.
This enclosure also enhances bass response and delivers a more focused, punchy sound, making closed-back headphones a popular choice for home listening, studio work, gaming, and commuting.
Personally, I prefer the closed-back design and often use models like the Sony ULT Wear, which I find excellent for its deep, punchy bass, effective noise isolation, and comfortable fit for long listening sessions, making it perfect for both work and leisure.
9. Open-Back Headphones
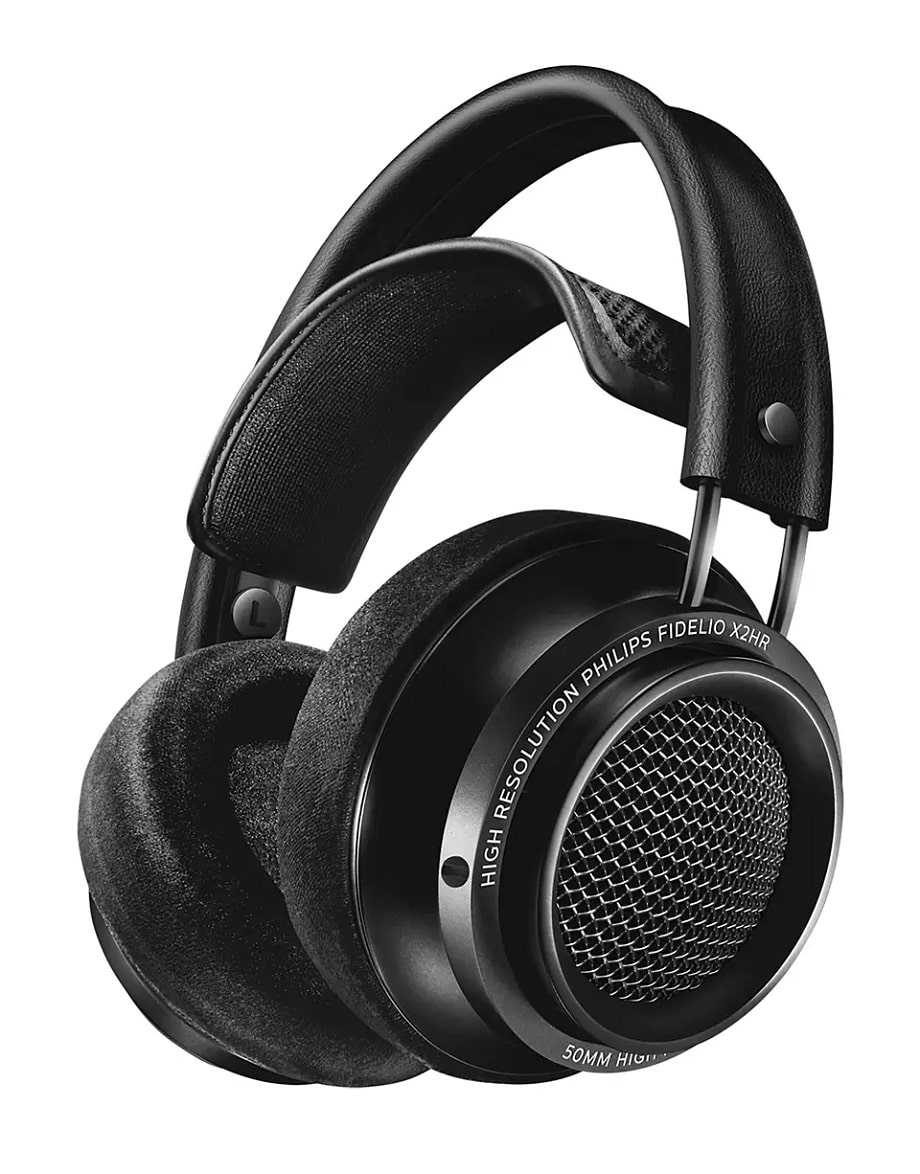

Open-back headphones, also known as open-air headphones, are designed with earcups that are perforated or partially open at the back, allowing air and sound to pass freely through the enclosure. This design creates a more natural, spacious, and airy sound with a wide soundstage.
However, this also results in sound leakage both in and out, making the music audible to others and allowing external noise to enter the listening experience. While this makes them ideal for enjoying high-quality music at home, they are not suitable for outdoor or noisy environments.
They are commonly used for home listening, studio mixing, and audiophile applications, with popular models including the Sennheiser HD600/HD650 and HD800/HD820S, Beyerdynamic DT990Pro, Audio-Technica ATH‑R70x, and AKG K701/K702.
10. Semi-Open Headphones
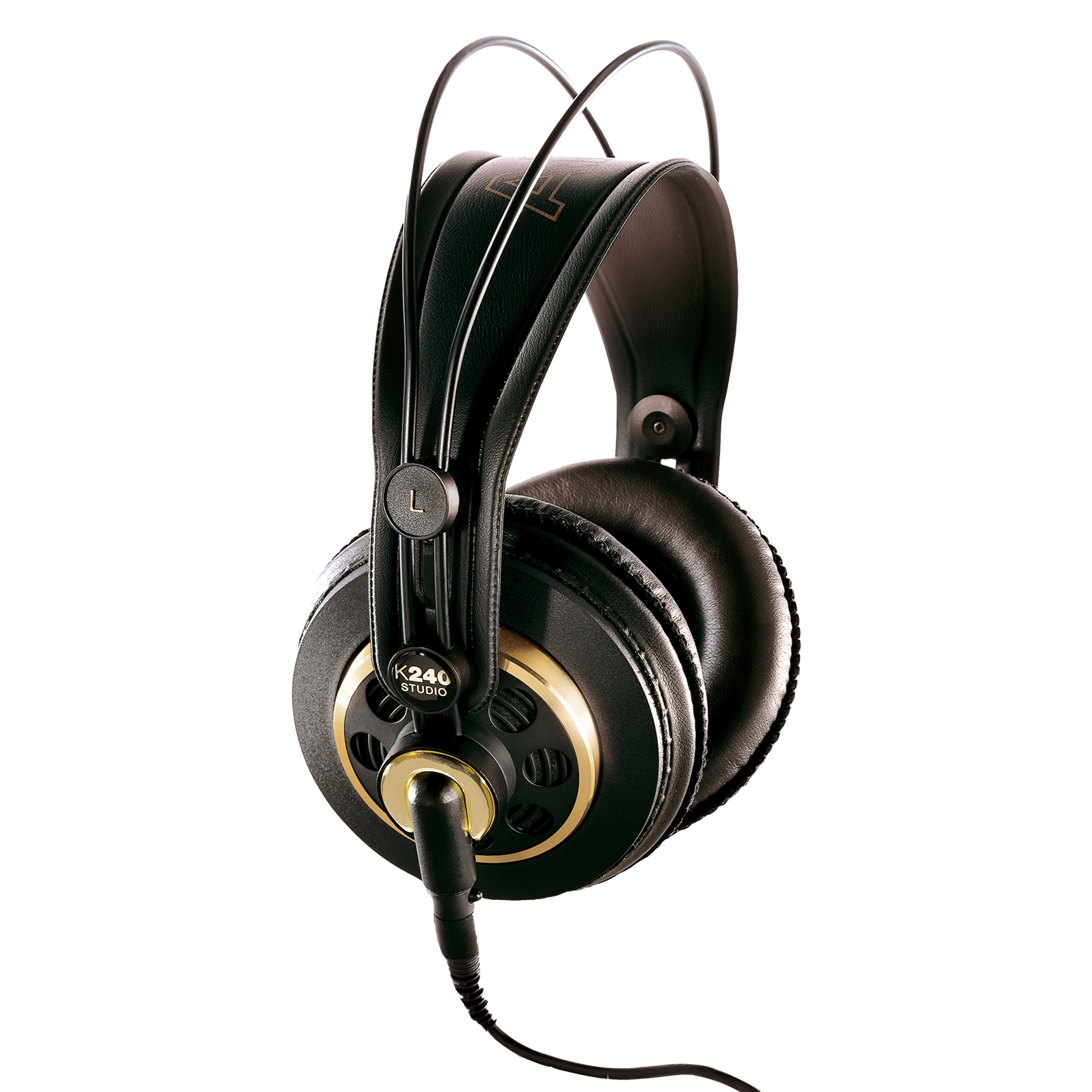

Semi-open headphones are designed with ear cups that combine features of both closed-back and open-back designs. Typically, the back of the ear cups is partially ventilated or perforated, allowing some air and sound to pass through while still maintaining some acoustic isolation.
This hybrid approach balances the spacious sound of open-back headphones with the isolation of closed-back headphones. Ideal for those who want a balance of clarity, detail, and comfort, making them suitable for home listening, casual studio work, and general audiophile use.
Different Types of Headphones by Connection
How headphones connect to your audio source plays a key role in their performance, how convenient they are to use, and which devices they work best with. The type of connection affects things like sound quality, latency, power delivery, compatibility, and mobility – making it an important consideration when choosing the right headphones. From traditional wired connections that offer zero latency and consistent audio quality, to modern wireless technology that offers freedom of movement and smart features, each connection method is designed for different listening needs and environments. Understanding these connection types will help you decide whether reliability, portability, or convenience are most important for your everyday use.
► Now, let’s explore the different types of headphones by connection, including wired and wireless options, and how each one works in real-world use, including:
11. Wired Headphones
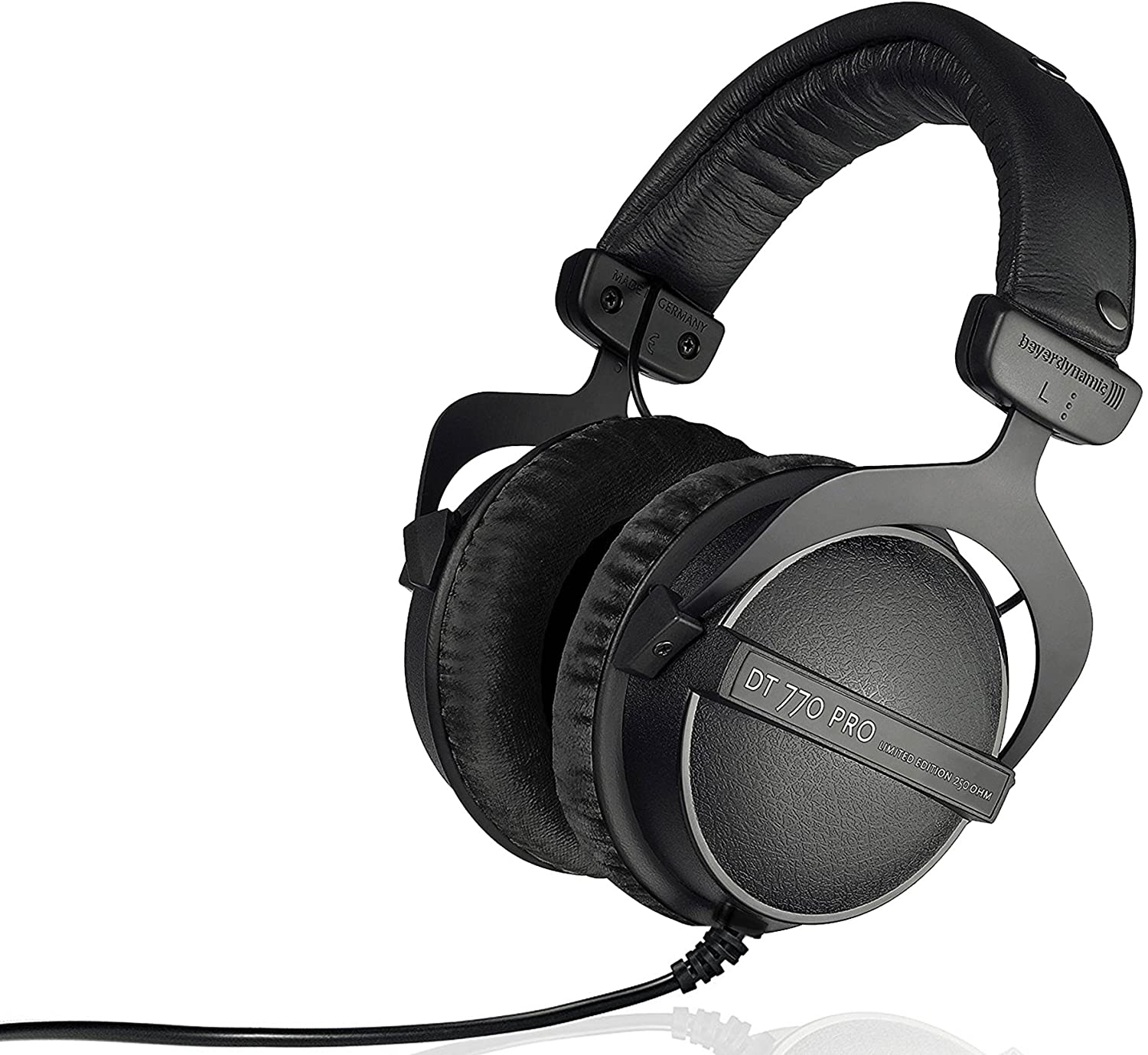

Wired headphones are audio devices—whether over-ear, on-ear, or in-ear—that connect directly to a source such as a smartphone, computer, audio interface, DAC, or music player using a physical cable.
Transmitting audio signals wirelessly without relying on compression or battery power, they receive continuous, direct power from the source and deliver high-fidelity sound, making them a preferred choice for professionals, audiophiles, and anyone who values reliable audio quality.
Wired headphones represent the original format of personal audio, dating back to telephone operators, but was revolutionized in 1958 when John C. Koss invented the world’s first stereo headphones, the SP/3 Stereophone, shifting the use of headphones from purely professional communication to immersive personal music enjoyment. While the market has seen a massive shift toward wireless, wired models remain the standard for audiophiles and professionals due to their uncompressed audio fidelity, zero latency, and complete connection reliability.
There are a variety of wired headphones available today, each featuring a different type of connection suited to specific devices and use cases. The connector type affects compatibility, audio quality, and sometimes the overall listening experience.
Below are the most common types of wired headphones by connections, includes:
- 3.5mm TRS Plug Wired Headphone: The 3.5mm TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) plug is the most widely used connector for consumer devices, including smartphones, laptops, portable music players, and tablets. It is compact, versatile, and supports stereo audio. While convenient, it typically lacks the enhanced shielding and robustness of professional connectors, but it remains ideal for everyday listening and casual use.
- 1/4-inch (6.35mm) Plug Wired Headphone: The 1/4-inch plug, also called 6.35mm, is larger and commonly used in studio gear, DJ players, professional amplifiers, and mixing consoles. It provides a more secure connection and is mechanically durable, making it ideal for high-stress environments like recording studios or live sound setups. Most modern headphones like Beyerdynamic DT 770 Pro or Audio-Technica ATH-M50x don’t come with a fixed 1/4-inch (6.35mm) plug by default. Instead, they usually include a detachable 3.5mm cable with a 1/4-inch adapter for studio or professional use.
- XLR / Dual XLR Plug Wired Headphone: XLR connectors are a staple in high-end audiophile and professional studio headphones. Dual XLR configurations offer separate left and right channels for better signal integrity and lower noise interference. These connectors are commonly used with headphone amplifiers, DACs, and professional mixing equipment to achieve precise, balanced audio reproduction. Examples include the Audio‑Technica BPHS1‑XF4 Broadcast Headset and the Audeze LCD-5 Audiophile Headphones, both of which take advantage of XLR connectivity for superior sound quality and reliability.
- USB / USB-C Plug Wired Headphone: USB and USB-C wired headphones transmit digital audio directly to the headphones, often including built-in DACs (Digital-to-Analog Converters) and microphones. They are popular with computers for office works and gaming setups, offering consistent sound quality without relying on the device’s analog output. Some models also support virtual surround sound, software customization, and integrated controls.
12. Wireless Headphones
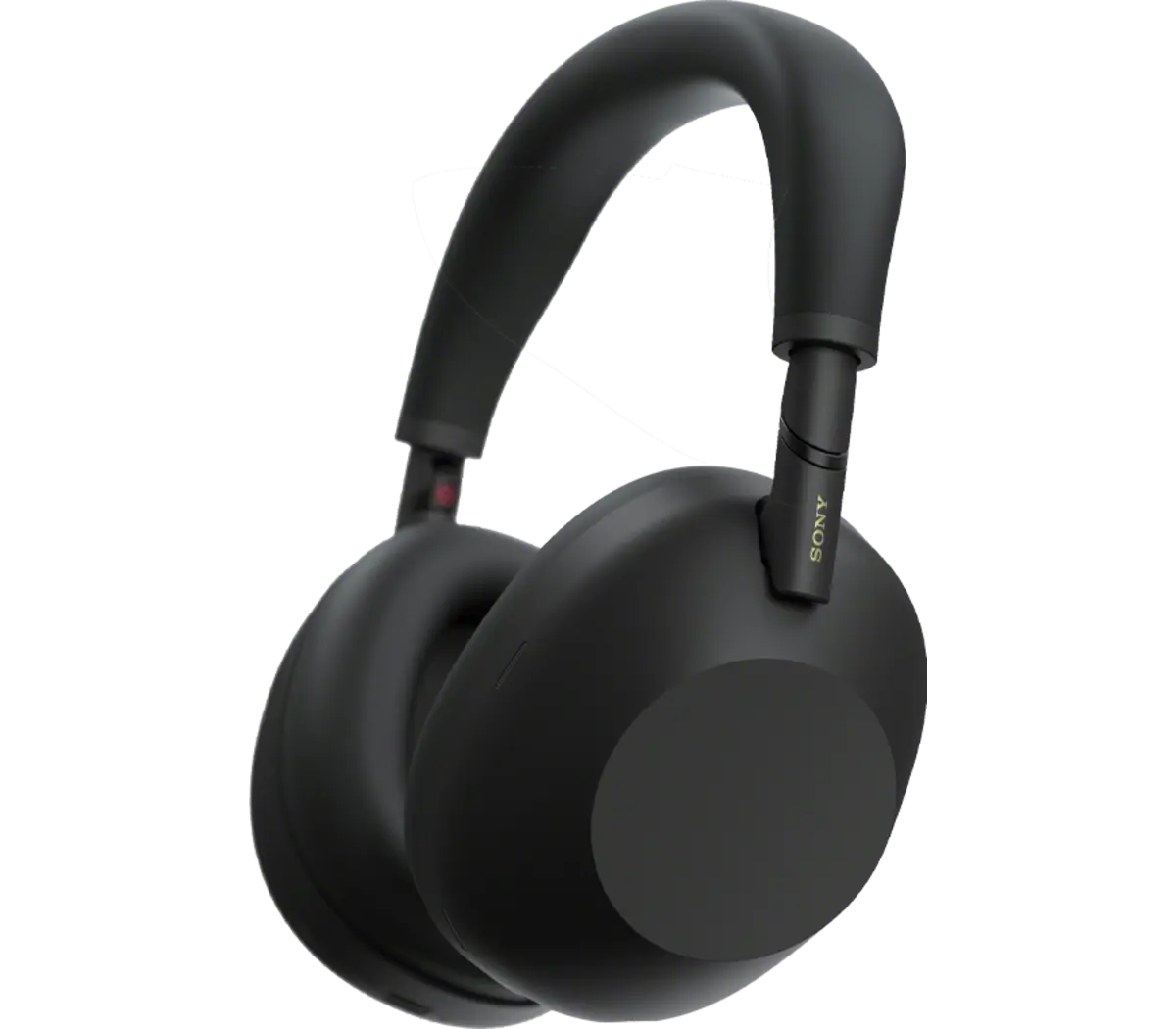

Wireless headphones are audio devices that connect to your music source without a physical cable, typically using Bluetooth, RF (radio frequency), or DECT wireless technology. These headphones have become increasingly popular due to the convenience of cable-free listening and the ability to move freely without being tethered to a device.
Unlike wired headphones, these types of headphones get their power from built-in batteries rather than drawing it directly from the audio source through a physical cable.
Many wireless headphones come with active noise cancellation (ANC), transparency/ambient modes, multipoint connectivity, and companion apps for sound customization. However, most models also include a wired port, which is useful when the battery runs out, making modern wireless headphones a practical and versatile choice over relying solely on wired headphones.
Industry-leading examples of wireless headphones include the Sony WH‑1000XM6 and Bose QuietComfort series, both of which set the standard for comfort, sound quality, and advanced features in the wireless audio market.
Below are the most common types of wireless headphones by connection technology, includes:
- Bluetooth Headphones: Bluetooth headphones are the most common wireless option for everyday use. They connect easily to smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other Bluetooth-enabled devices, offering freedom from cables. Some models transmit audio wirelessly to a dedicated USB dongle (also called 2.4 GHz wireless), or operate entirely without a dongle (often called standard Bluetooth or advanced Bluetooth codecs like aptX HD or LDAC, ensuring precise, high-fidelity sound) connection. They often feature built-in batteries, basic onboard controls, and sometimes advanced features like ANC and app-based customization. Both transmit audio without cables, but USB-dongle models often provide lower latency, a more stable connection, and better performance on PCs or gaming and office works, while Bluetooth headphones offer universal compatibility and convenience for everyday devices.
- Wi-Fi (WLAN) Headphones: Wi‑Fi headphones connect to a source device via a local Wi‑Fi network or a dedicated Wi‑Fi transmitter. Unlike Bluetooth, which has limited range and bandwidth, Wi‑Fi can provide higher-quality audio, lower latency, and longer range, making them ideal for home audio setups, multi-room streaming, or high-fidelity listening. Headphones like Sonos Ace utilize a dedicated point-to-point Wi-Fi connection for the “TV Audio Swap” feature with compatible Sonos soundbars. They do not connect to a home Wi-Fi network like a typical Sonos Speaker to stream music around the home. And many others example includes Sennheiser RS 195, Sony WH-L600, and some Bowers & Wilkins PX7 Wireless headphones. Which are typically used RF Wireless technology and Bluetooth technology as a main wireless technology.
- RF (Radio Frequency) Headphones: RF headphones use a dedicated radio frequency transmitter to send audio to the headset, typically over 2.4 GHz. They offer longer range and low latency, making them ideal for home TV, audio systems, or casual listening. The dedicated transmitter ensures a stable connection, but they are generally less portable. Examples include Sennheiser RS 175 and Sony MDR-RF855RK.
- DECT Headset: DECT (Aka Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications) headsets are wireless audio devices that use a dedicated DECT base station to transmit audio instead of Bluetooth or RF. They operate on their own frequency band (typically 1.9 GHz), which keeps them free from Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and mobile network interference. This gives excellent range, stable connectivity, and ultra-low latency, making them ideal for office calls, customer support centers, and professional communication setups. The most common DECT wireless headphones example are: Jabra Engage 65/75 series, Yealink WH62 and more.
- Infrared (IR) Headphones: RF headphones use a dedicated radio frequency transmitter to send audio to the headset, typically over 2.4 GHz. They offer longer range and low latency, making them ideal for home TV, audio systems, or casual listening. The dedicated transmitter ensures a stable connection, but they are generally less portable. Examples include Sennheiser RS 175 and Sony MDR-RF855RK.
With that, we’ve covered nearly all major types of wireless headphone technologies currently available as a reference.
Different Types of Headphones by Driver Technology
At the heart of every headphone is its driver—the component responsible for converting electrical audio signals into the sound waves you hear. Different driver technologies use different physical designs and operating principles, which directly affect the sound quality, clarity, bass response, efficiency, and even the size and price of the headphones. Understanding how each driver type works can help you choose headphones that match your listening preferences, whether you prioritize powerful bass, detailed mids, a wide soundstage, or ultra-accurate audio reproduction.
► Now, let’s explore the different types of headphones based on driver technology and understand how each one produces sound and shapes the listening experience, including:
13. Dynamic (Moving-Coil) Driver Headphones
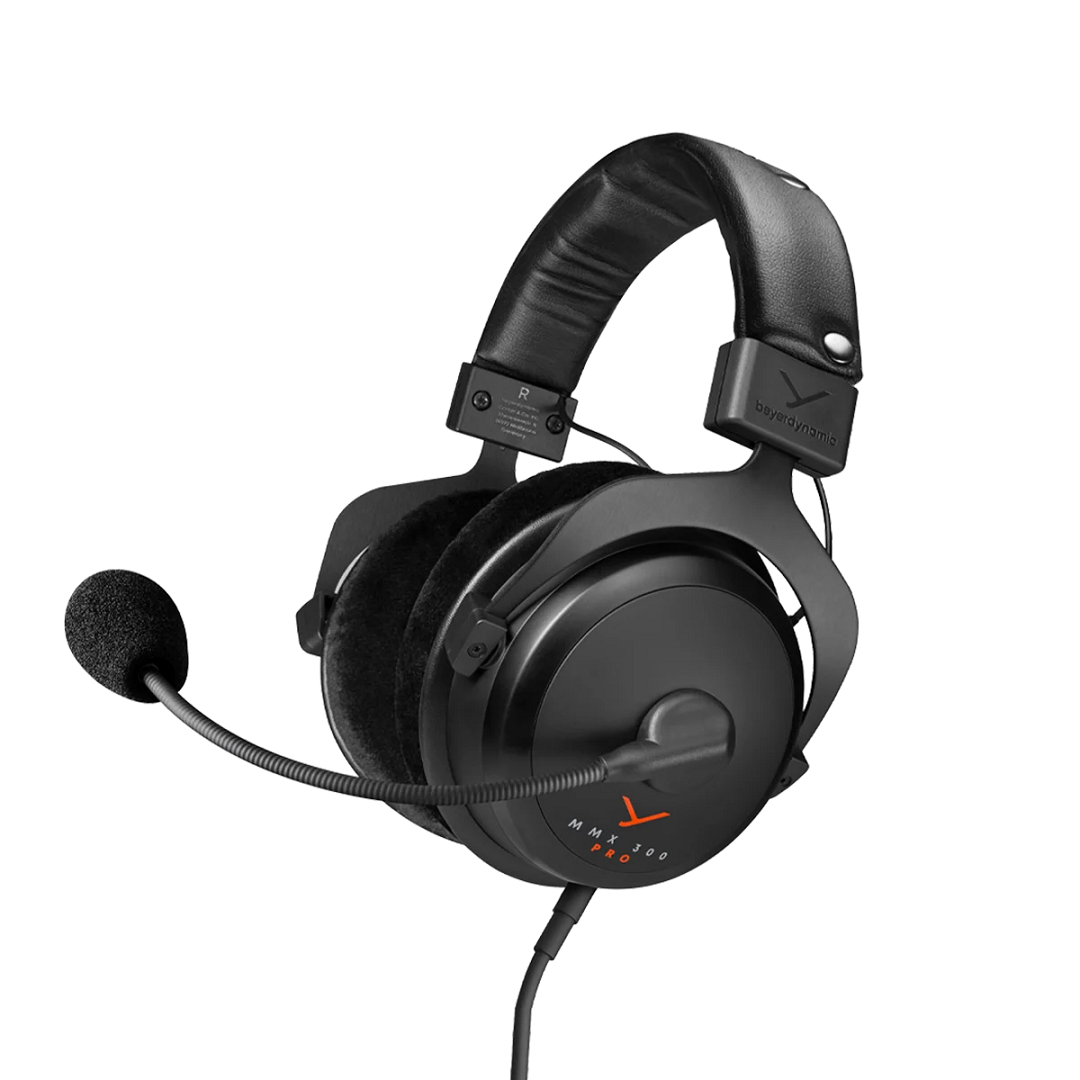

Dynamic drivers are the most common headphone driver type, using a voice coil, magnets, and diaphragm to convert an electrical audio signal into audible sound waves to produce sound. They are known for producing strong bass, high volume output, and good overall balance. Because they are affordable and energy-efficient, they are used in everything from budget earbuds to high-end studio headphones. Their simple design makes them durable and reliable for everyday use.
Headphones like beyerdynamic MMX 300 PRO uses dynamic drivers, specifically the proprietary STELLAR.45 driver. These dynamic drivers are designed to deliver high-quality audio for both gaming and music, providing a balanced sound profile with deep bass and clear treble.
14. Planar Magnetic (Orthodynamic) Driver Headphones
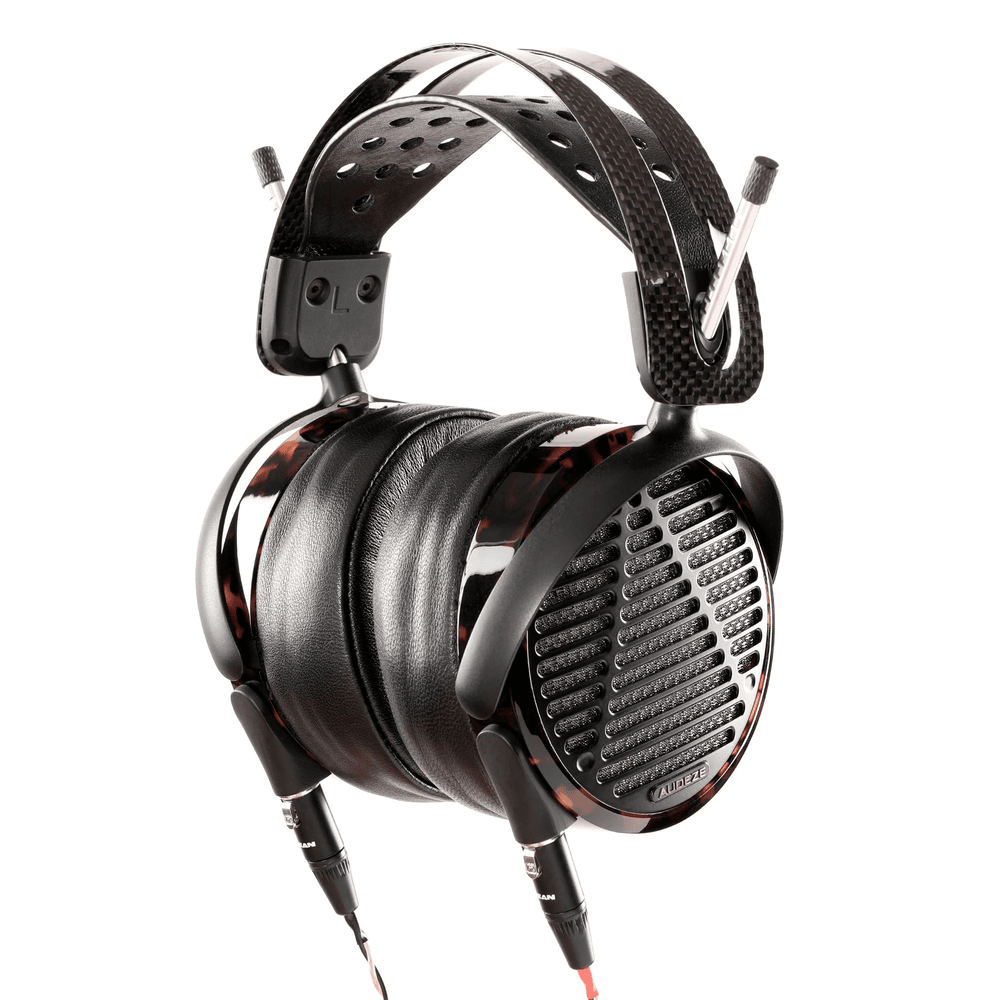

Planar Magnetic headphones, sometimes historically referred to as Orthodynamic, Isodynamic, or Magnetostatic headphones, are a unique and highly respected driver technology widely appreciated in the high-fidelity audiophile community.
Unlike traditional dynamic drivers, planar magnetic drivers use a thin, flat diaphragm embedded with conductive traces, suspended between arrays of powerful magnets. This design allows the diaphragm to move evenly across its entire surface, producing extremely accurate sound, very low distortion, and exceptional detail—especially in the midrange and high frequencies. This also tend to offer a wider, more spacious soundstage and tight, controlled bass compared to typical dynamic drivers.
However, because these drivers require strong magnetic structures and more power to perform optimally, they often larger, less portable, and typically rely on dedicated headphone amplifiers or DAC/amps to achieve their full potential.
You can consider choosing from the many well-known planar magnetic headphones available today. Brands like Audeze and HiFiMAN are at the top of the list.
16. Electrostatic Driver Headphones
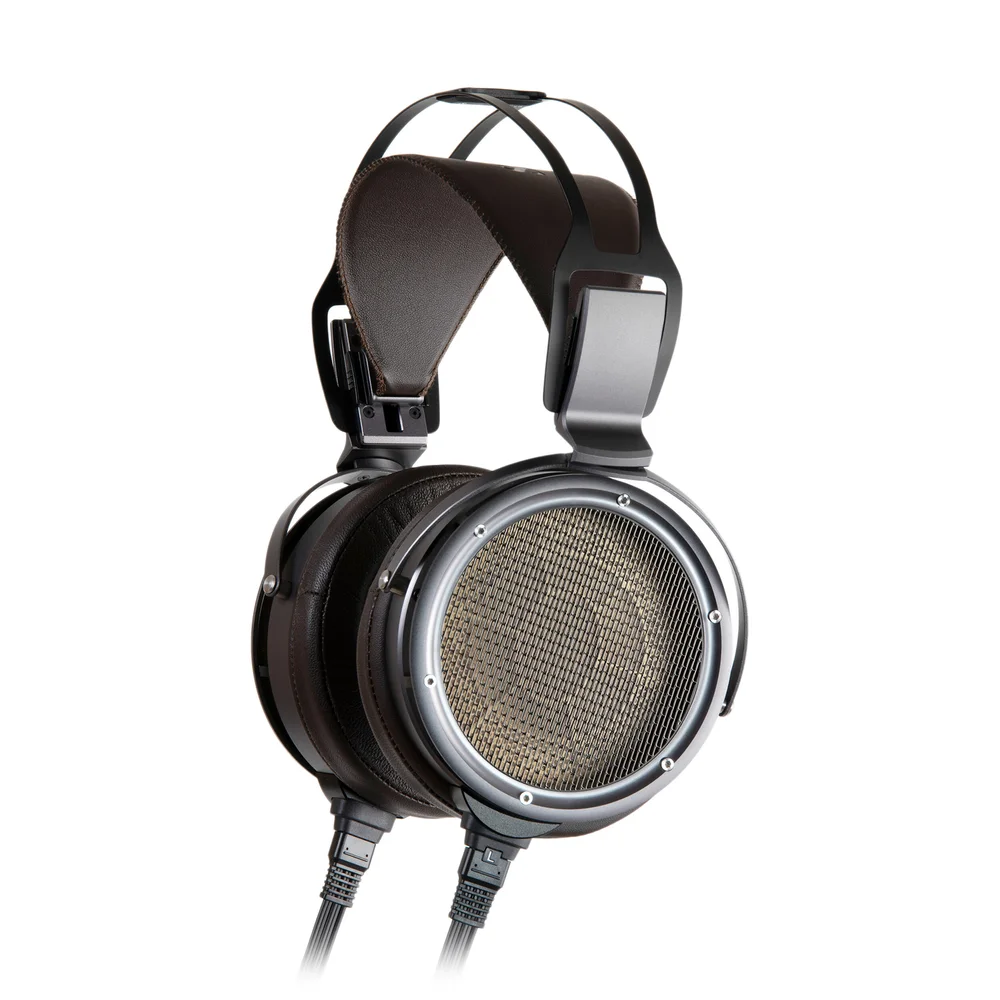

Electrostatic (EST) headphones use an ultra-thin diaphragm hanging between two electrically charged stator plates, which are propelled by electrostatic force rather than traditional electromagnetism. This design produces exceptionally clear, fast, and distortion-free sound – often considered the most transparent and realistic listening experience available.
Because they require dedicated high-voltage electrostatic amplifiers and specialized setups, it remain a premium, niche choice. Nevertheless, they are highly prized by audiophiles and engineers seeking the highest levels of detail and accuracy.
Popular models include Stax SR-X9000, Moondrop ZERO, Audeze CRBN/CRBN2.
17. Balanced Armature Drivers Headphones
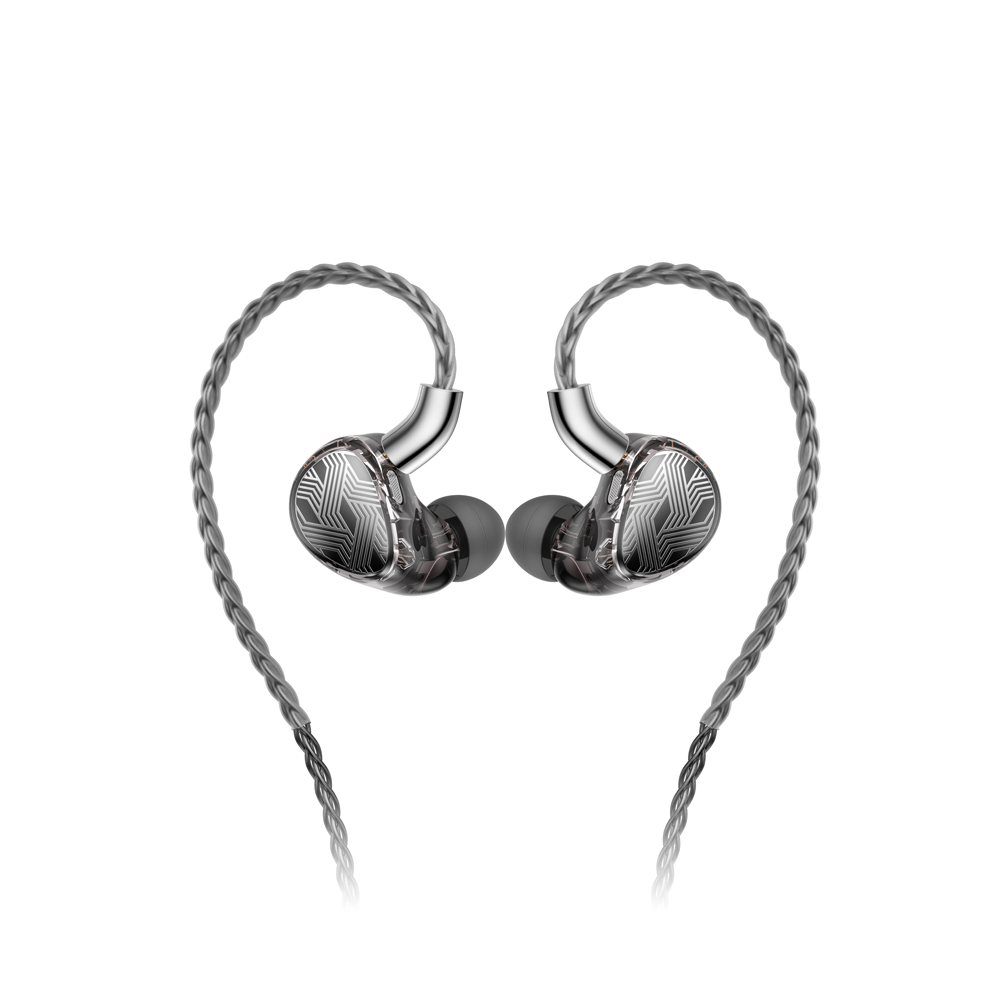

Balanced Armature (BA) drivers are a unique type of transducer technology that is almost exclusively found in In-Ear Monitors (IEMs) and high-end hearing aids due to their incredibly small size, high sensitivity, and specialized sound characteristics.
They use a miniature armature that pivots inside a magnetic field to move a diaphragm, resulting in extremely detailed and efficient sound. They excel at reproducing mids and highs with clarity but often lack deep bass unless paired with other driver types like Dynamic drivers.
Popular models include FiiO FA19, KZ AS10/BA10, Shure SE846.
18. Hybrid Drivers Headphones
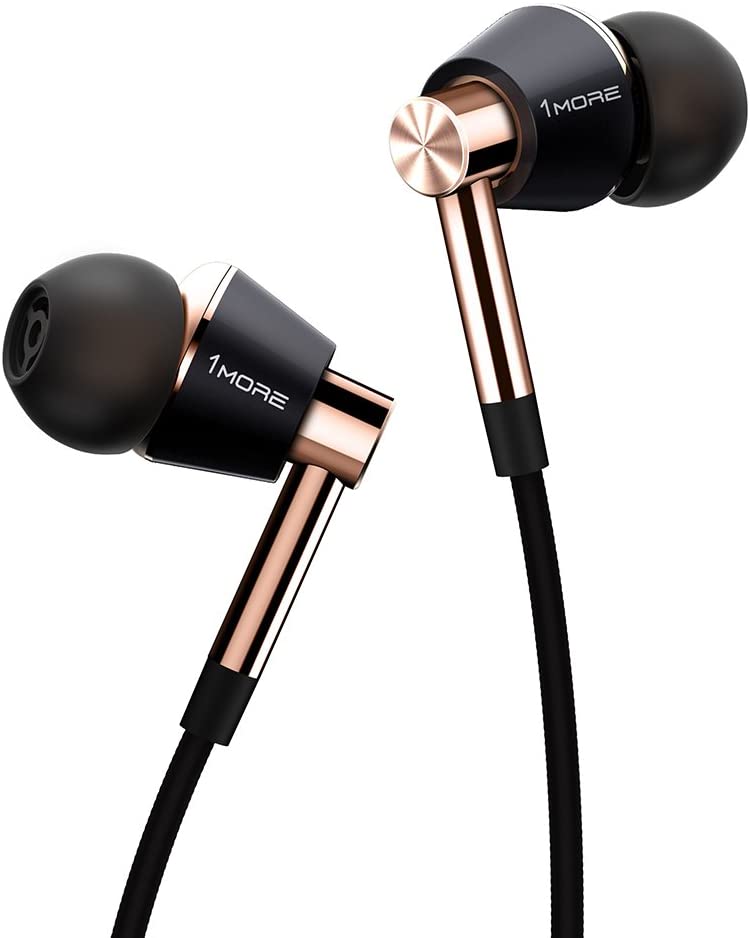

Hybrid driver headphones combine two or more driver technologies—most often a dynamic driver for bass and balanced armatures for clarity. This combination delivers a wider frequency range and a more refined listening experience than using a single driver type.
Hybrids are popular in modern IEMs where manufacturers use multiple BAs and one dynamic driver to achieve “best of both worlds.” They offer excellent detail without sacrificing low-end performance.
Many well-known hybrid models you can buy right now include the 1MORE Triple Driver, Sony IER-Z1R, FiiO FH7, and KZ ZS10 Pro in-ear monitor headphones.
Different Types of Headphones by Professional Purpose
Headphones are often designed with specific professional environments in mind. These purposes prioritize accuracy, durability, communication features, or isolation, depending on the task. Below are the most common professional-grade headphone categories and what makes each one unique.
► Now, let’s explore the different types of headphones based on their professional purpose and intended use, including:
19. Aviation Headphones
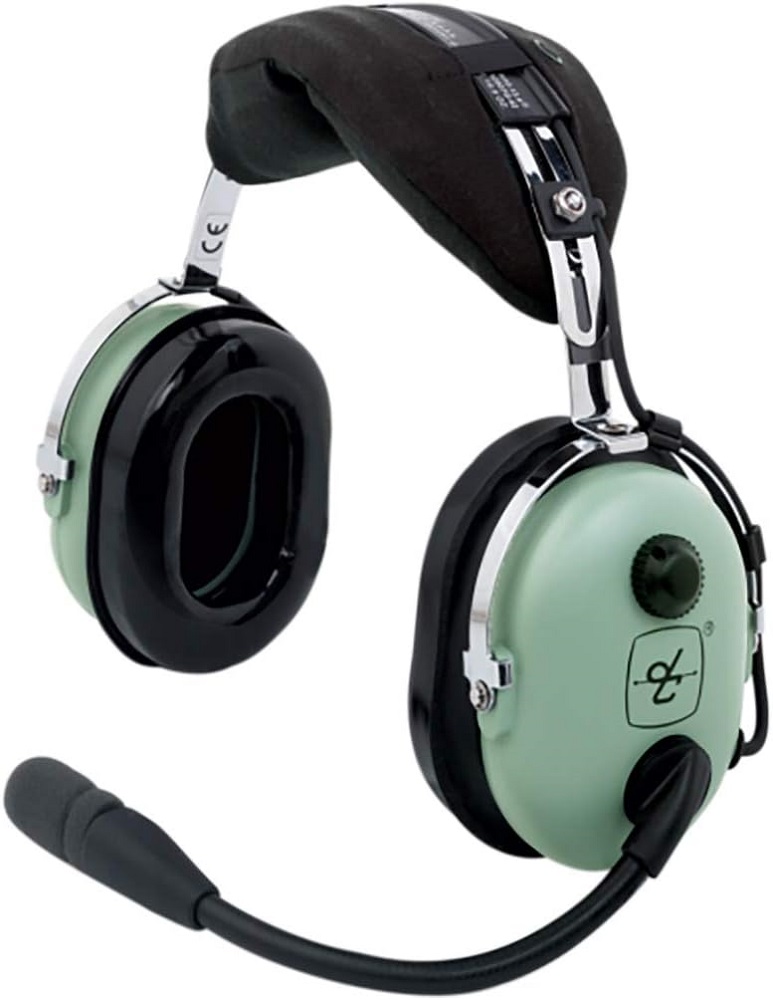

Aviation headsets are specialized headphones designed for pilots and aircrew. They provide clear communication with air-traffic control and reduce cockpit noise using powerful passive or active noise reduction. They often include a microphone, durable build quality, and aircraft-specific connectors. They are essential equipment for flying, but are not used for regular consumer listening.
Popular models include the Bose A20, David Clark H10-13.4, and Lightspeed Zulu 3, which are industry standards for both commercial and private aviation.
20. Broadcast Headphones
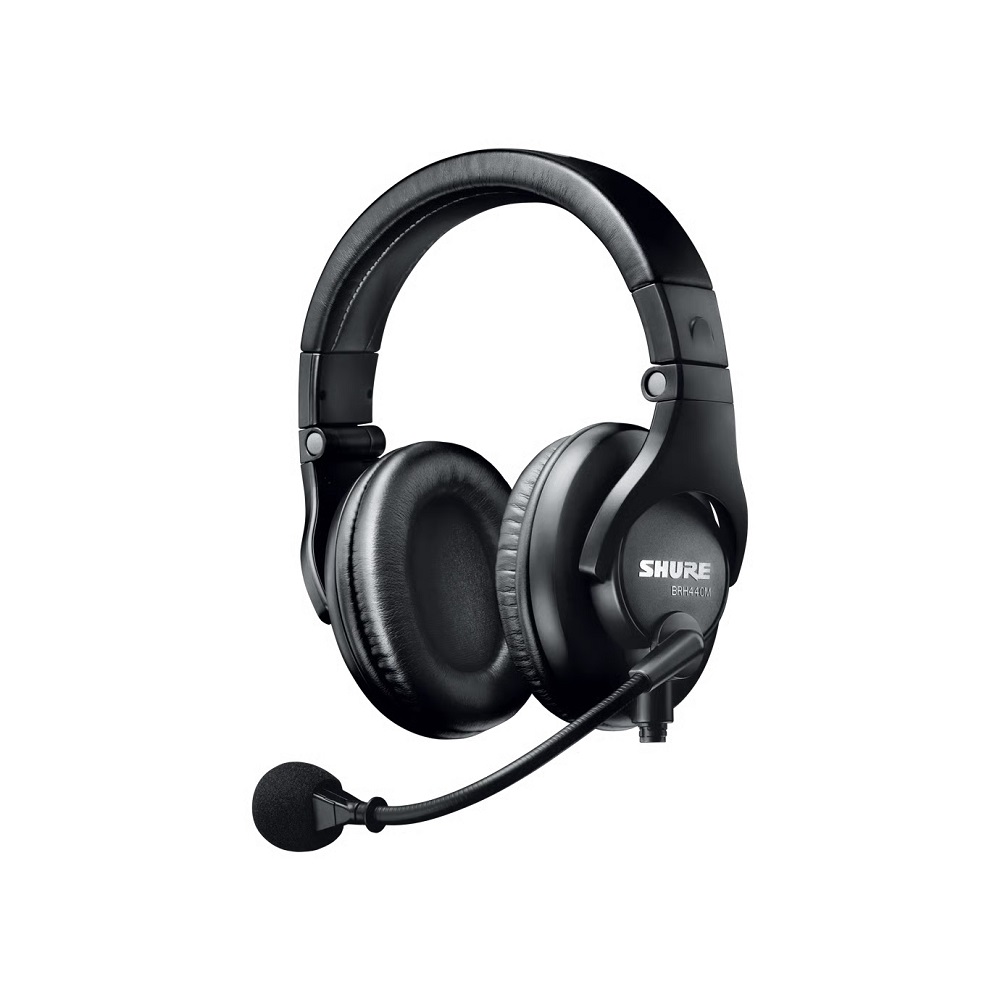

Broadcasting headphones are specially designed for commentators, voice-over artists, and live broadcast professionals. These headsets combine high-quality headphones with built-in microphones that deliver clear, consistent voice capture. They offer strong isolation and durability for long production days. Some notable models includes Shure BRH440M, Audio-Technica BPHS1, and Sennheiser HMD 300 PRO.
21. Office / Call Centers Headphones
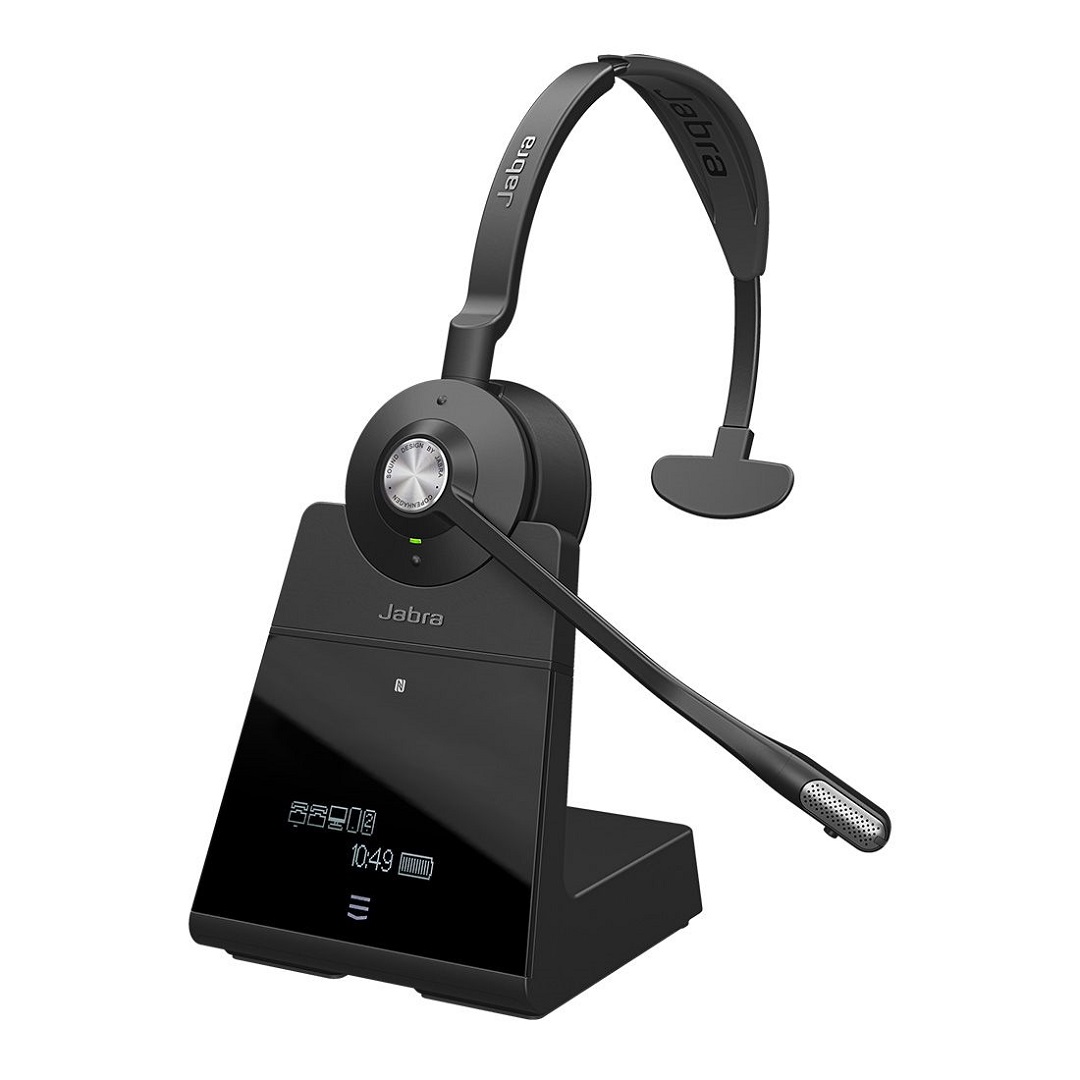

Office and call-center headphones are designed specifically for long hours of voice communication, offering comfort, clear microphone quality, and noise reduction for busy work environments. They often include features like noise-canceling boom mics, lightweight headbands, and soft earpads to minimize fatigue during extended use.
Many models, including Jabra and Poly (Plantronics), support UC (Unified Communications) platforms such as Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and Cisco, ensuring reliable call quality and seamless integration with business communication systems. These headsets are widely used in offices, call centers, and remote work setups where consistent performance and all-day comfort are essential.
22. Medical / Healthcare Headsets

Medical or healthcare headsets are specialized audio headset devices designed for medical professionals, telehealth practitioners, and hospital staff. Especially those who need clear, reliable communication in clinical environments. These headsets are optimized for voice clarity, noise reduction, and comfort during long shifts, allowing doctors, nurses, and telehealth providers to communicate accurately without distraction.
These type of headset provide long-term comfort, and hygiene, featuring noise-cancelling microphones, lightweight over-ear or on-ear designs, and easy-to-clean materials. Popular examples include the Plantronics (Poly) Blackwire 8225, Jabra Evolve2 65, and Sennheiser SD Pro 2.
23. Studio Monitor Headphones

Studio monitor headphones are professional-grade headphones designed to deliver a neutral, accurate, and uncolored sound signature. Unlike consumer headphones that enhance bass or treble, studio monitors aim to reproduce audio exactly as it was recorded, making them ideal for mixing, audio and video editing, tracking, and critical listening in production environments. They aim for accuracy, detail, and clarity rather than entertainment-focused tuning.
Most studio monitors use a closed-back design to prevent sound leakage during recording, although open-back models are preferred for mixing and mastering due to their wider, more natural soundstage. Examples include the Sony MDR-7506, Audio-Technica ATH-M50x, Beyerdynamic DT 770 Pro, Sennheiser HD 600 (open-back), and AKG K240 Studio.
24. Military / Tactical Headsets

Military or tactical headsets are specialized communications and hearing protection devices designed for use in defense, law enforcement, and tactical operations. They combine clear audio communication, noise reduction, and situational awareness in challenging or high-noise environments.
These types of headsets are commercially available but are often custom-made depending on the needs of the military or organization, with connectivity technology that may be proprietary, wired, or specialized RF wireless to ensure secure, reliable, and low-latency communication. Some common examples include the Peltor ComTac III, 3M Peltor Tactical XP, and Ops-Core AMP communication headset.
25. DJ Headphones

DJ headphones are specialized headphones designed specifically for disc jockeys, professional mixers, and performers who need precise, reliable audio monitoring in loud, dynamic environments. They are designed to handle high sound pressure levels, provide accurate bass response, and allow DJs to cue and mix tracks effectively.
While a DJ can technically use any headphones, most consumer or casual headphones are not designed for the high SPLs (sound pressure levels), durability, one-ear monitoring, accurate bass response, and reliable connectivity — such as an XLR or 1/4-inch TRS plug — that professional DJ headphones require for live performance and mixing.
So, if you’re a DJ or aspiring to mix professionally, you should consider a reliable, foldable pair of DJ headphones with rotating ear cups for one-ear monitoring, such as the Sennheiser HD 25, Pioneer DJ HDJ-X10, or Audio-Technica ATH-M50x.
26. Industrial Earmuff Headsets

Industrial headphones are specialized communication headset designed for noisy work environments such as factories, construction sites, or airports. They combine hearing protection with clear two-way communication, often integrating microphones for intercoms, radios, or other industrial communication systems. And typically use wired, DECT, or RF wireless connections for reliable, low-latency communication in challenging environments.
Different Types of Headphones by Use Cases
When choosing headphones, the ideal option often depends on how and where you plan to use them. Different environments – such as commuting, gaming, working out, studio recording, or office calls – require different features such as noise cancellation, comfort, durability, microphone quality, or water-resistance. For this reason, many brands design headphones that are specifically optimized for specific use cases, making it easy for users to get the best experience without compromise.
► Now, let’s explore the different types of headphones designed for specific use cases and see which ones best match your daily activities, including:
27. Sports / Running Headphones

Sports and running headphones are specifically designed to meet the demands of physical activity. Unlike regular headphones, which focus only on sound quality and comfort for stationary use, running headphones are designed to be durable, secure, and safe during vigorous movement.
They typically feature sweat- and water-resistant designs, secure ear hooks or wing tips, and lightweight construction to stay in place during running or walking.
28. Workout / Gym Headphones

They emphasize a strong base, secure fit, and durability, often offering IP ratings for sweat and dust resistance. They typically include in-ear or ear-hook designs that stay stable during fast movements and weight training. In all of these cases, wireless neckband earbuds, true wireless earbuds, and on-ear headphones are more prevalent.
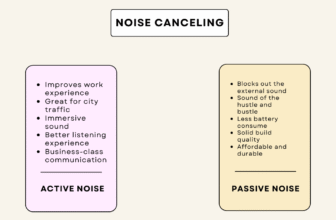
29. Noise-Canceling Headphones

Noise-cancelling headphones are audio devices designed to reduce or eliminate unwanted ambient background sounds, allowing you to hear your music, calls, or simply enjoy silence with much greater clarity. There are three main types of noise-cancelling technologies available today, let’s explore each one now:
- Active Noise Cancellation (ANC): ANC headphones use a built-in microphone and digital signal processing to create an inverse (“anti-noise”) sound wave that cancels out static, low-frequency sounds like engines or fans. They include a physical on/off button, which allows users to switch between noise-canceling mode, passive mode, or transparency/ambient mode depending on the environment.
- Passive Noise Cancellation: Relies on the physical design of the headphone (thick earcups, snug ear tips) to create a tight seal and physically block out noise.
- Adaptive ANC: An advanced form of ANC that uses real-time monitoring to automatically adjust the level and type of noise cancellation based on your changing environment. Some headphones implemented these advanced features. For example, Bose….
30. Gaming Headphones
Gaming headphones (or gaming headsets, if they have a microphone) are audio devices specifically designed for video games, offering clear positional audio, powerful bass, and built-in communication features for multiplayer gameplay. They prioritize directional sound so players can hear footsteps, gunfire, or spatial cues, which helps increase in-game awareness.
Most gaming headsets have a boom microphone for team chat, along with features like virtual surround sound, customizable EQ, RGB lighting, and low-latency wireless USB connectivity for plug-and-play support on PCs and consoles, and most models use an over-ear design for better isolation and comfort during long gaming sessions.
Some top gaming headset models include the SteelSeries Arctis Nova Pro, Razer BlackShark V2 & Razer Kraken Kitty series, Logitech G Pro X, and HyperX Cloud Alpha.
31. VR / AR Headphones

VR (virtual reality) and AR (augmented reality) headphones are specialized audio devices designed to deliver 3D spatial sound that matches what you see in a VR headset or AR glasses. They create the illusion that sounds are coming from the right direction – above, behind, far away, or swirling around you – which enhances realism and immersion.
These headphones typically feature low-latency wireless connectivity, advanced spatial audio processing, and large size for long VR sessions. They are commonly used for gaming, simulations, training, virtual meetings, and other interactive digital experiences.
Popular models include Meta Quest, HTC Vive, and Sony PlayStation VR2.
32. Audiophile Headphones

Audiophile headphones are high-fidelity (hi-fi) headphones designed for listeners who want extremely accurate, detailed, and natural sound reproduction. Rather than boosting bass or altering frequencies, they aim to reproduce audio exactly as it was recorded, with a wide soundstage, high-resolution drivers, and premium materials.
They are built for music enthusiasts, known as “audiophiles,” – those who are interested in high-quality sound – use these headphones for critical listening, musical appreciation, and studio-grade clarity.
They are often open-back and wired, which provide a more spacious and natural sound, although closed-back and Bluetooth versions also exist. Due to their high impedance or specialized driver design, they usually require a dedicated DAC or amplifier to achieve their full performance.
As a result, these headphones can handle higher sound levels with minimal distortion, delivering precise and detailed audio that exceeds the capabilities of most consumer headphones at the same volume.
Some great audiophile headphones include Sennheiser HD 600 and HD 800S, Beyerdynamic DT 1990 Pro, Audeze LCD-X, Focal Clear MG.
33. Kids’ Headphones

Kids’ headphones are specialized headphone built with hearing protection as the top priority, featuring volume-limiting technology for safer listening, durable construction to withstand everyday use, and comfortable, soft-padded earcups designed for small heads and extended wear.
Popular examples of kids’ headphones include the Puro Sound Labs BT2200 (known for its strict volume limits), the JLab JBuddies (durable and budget-friendly), and the BuddyPhones School+ (designed for safe listening with a built-in microphone for online classes).
34. Hearing Aids Headsets

Hearing-aid headphones – also known as assistive listening headphones or personal sound amplification products (PSAPs) – are audio devices designed to help people with mild hearing loss hear clearer everyday sounds, speech, and media.
They use built-in microphones, amplification circuitry, and noise-reduction features to enhance speech and reduce background noise, making it easier to understand conversations, TV audio, and calls.
However, they are not medical hearing aids. A standard pair of headphones or earbuds with hearing-aid features cannot replace a professionally fitted medical hearing aid. These are controlled medical devices that are precisely programmed to match an individual’s specific hearing-loss profile across many frequencies, while “hearing-aid headphones” or assistive earbuds only provide general amplification and comfort for mild hearing loss – not clinical correction.
35. Translation / Interpreter Headsets
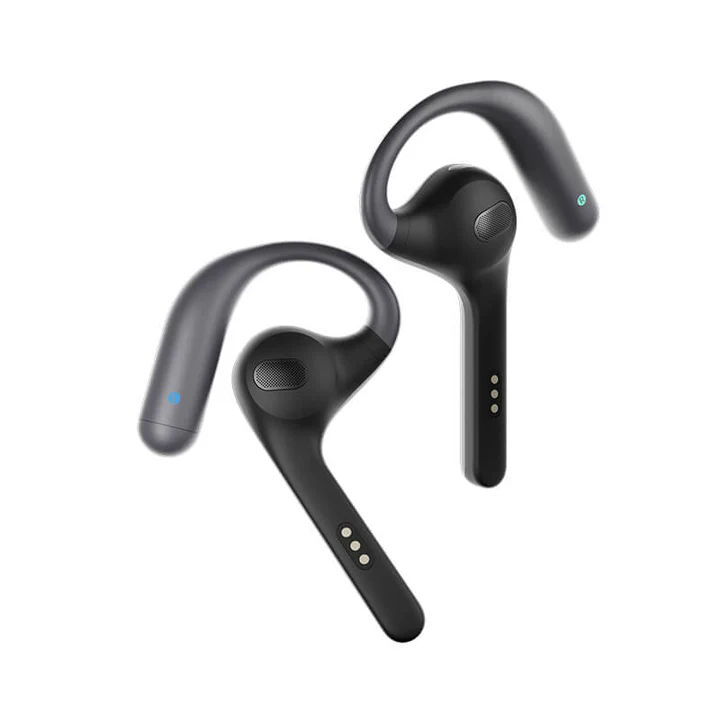

Translation or interpreter headsets are specialized audio devices used in conferences, meetings, multilingual events, political discussions, courtrooms, and international communication settings. They are designed to clearly convey real-time translated speech to the audience, while simultaneously reducing background noise and ensuring speech intelligibility.
These systems typically include a transmitter (from the interpreter), a receiver (for the listener), and lightweight headphones or earpieces that are optimized for voice clarity over music quality. They prioritize long-term comfort, low latency, stable wireless transmission, and clear voice reproduction so that participants can effortlessly follow conversations in different languages.
Popular examples include the Timekettle W4 Pro and Tagry K08, features depending on the environment and area of use.
36. Study / Focus Headphones
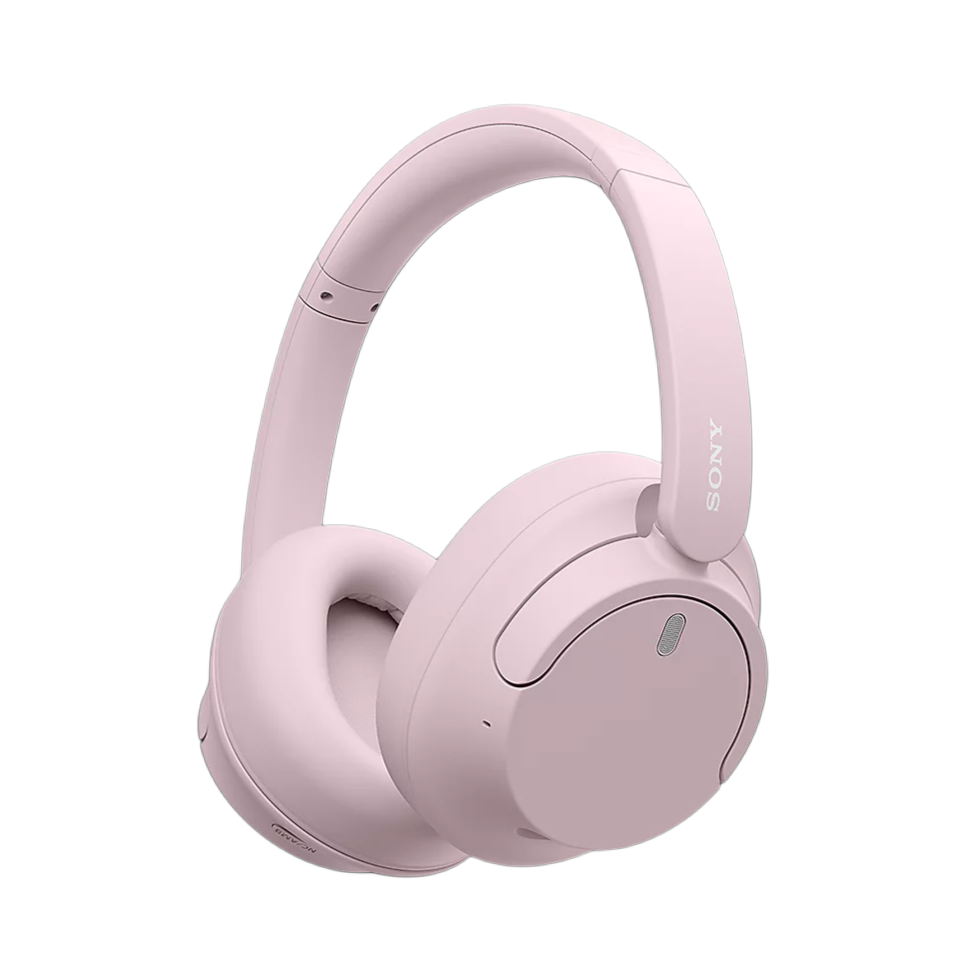

Study or focus headphones are designed to help users focus, reducing distractions while reading, studying, remote learning, or deep work. They often feature passive isolation or ANC, a lightweight design that is comfortable for long-term use, and a balanced sound profile to avoid fatigue.
Some models include transparency mode, white-noise or focus sound features, and long battery life to support increased productivity. Examples includes Sony WH-1000XM series, Bose QuietComfort, and Anker Soundcore Life Q30.
37. Sleep Mask Headset
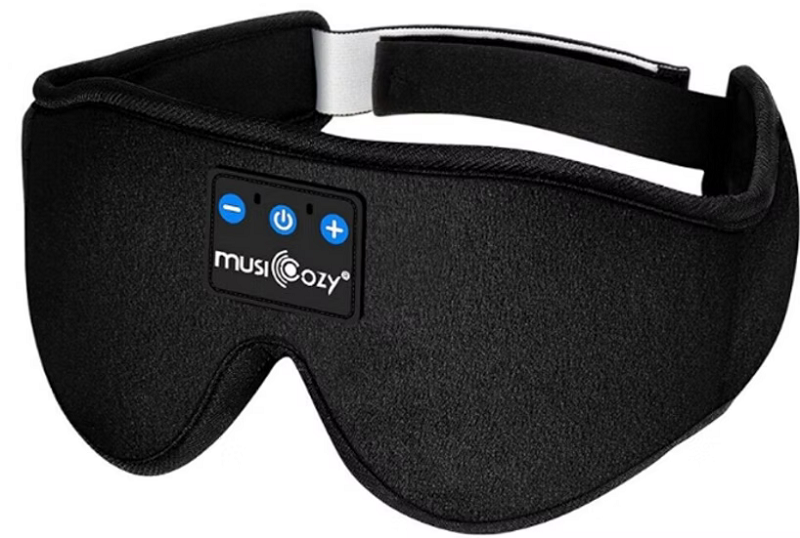

Sleep mask headphones are wearable audio devices built directly into a soft, padded sleep mask. Instead of traditional earcups or ear tips, they use ultra-thin flat speakers placed near the ears inside the fabric, delivering comfortable audio while sleeping without putting pressure on the ears.
These headphones are specially designed for side sleepers, meditation, and relaxation. Most models are Bluetooth-enabled, lightweight, washable, and focus on comfort and convenience rather than high-end audio quality.
One of the most popular options is the MUSICOZY 3D Bluetooth Sleep Mask, which combines a soft, contoured eye mask with built-in flat speakers and Bluetooth connectivity — delivering up to 10+ hours of stereo audio without pressure on your eyes.
Now, let’s explore how to find the best headphones below!
How to Choose the Right Types of Headphones for Your Needs?
When choosing headphones, the right model depends on your lifestyle, usage patterns, comfort preferences, and sound needs. Below is a structured analysis to help you identify exactly what is important before making a purchase.
1. Determine Your Use Case (Primary Purpose)
Before buying headphones, identify what you will be using them for, such as music production, gaming, travel, workouts, office calls, or casual listening. Each use case requires different features, such as low latency USB wireless headsets for working from home, zero-latency wired headphones for gaming, comfortable on-ear designs for long office calls, ANC Bluetooth headphones for traveling, or over-ear/water-resistant earbuds for workouts. Knowing your primary purpose helps you choose the right type without overpaying for features you don’t actually need.
2. Choose the Right Form Factor & Design
Choosing the right form factor is essential for comfort, fit, and sound experience. Depending on your daily activities and personal comfort, consider whether you prefer over-ear, on-ear, in-ear (earbud) or truly wireless designs.
For over-ear headphones, the enclosure design is important: Closed-back headphones isolate sound and prevent leakage, making them ideal for commuting or noisy environments, while open-back headphones provide spacious, natural sound and a wide soundstage, perfect for listening at home or working in the studio room. Additionally, features like foldable designs, lightweight construction, and adjustable headbands contribute to overall comfort and portability.
3. Wired vs Wireless: Choose Which Connection Technology Do You Need
Wired headphones offer zero latency, stable audio, and often better fidelity, making them ideal for studio work or critical listening. Wireless headphones offer convenience, freedom of movement, and smart features like ANC or multipoint pairing. Choose based on whether you prioritize sound accuracy or everyday convenience.
4. Check Driver Type & Sound Signature
Dynamic, planar magnetic, balanced armature, and hybrid, or other driver types can dramatically affect clarity, bass, and overall sound. Knowing your preferred sound signature (bass-heavy, neutral, warm, bright) can help you choose the right model.
5. Active vs. Passive: Choose Which Isolation Works Best for You
Active noise cancellation (ANC) is ideal for travel, commuting, or other noisy environments, while passive isolation relies on the physical sealing of the earcups or ear tips. Choose based on how much external noise you want to block out.
Many high-quality noise-cancelling headphones can block up to 90% of it’s external noise without ANC, while ANC offers additional electronic cancellation for low-frequency noise that is useful for aireplane; for example, the SONY ULT Wear combines both passive and ANC performance effectively.
6. Comfort & Build Quality: Verify Headset Earcups and Materials
Comfort is crucial for long-term listening—check the softness of the ear padding, the pressure of the headband, and the overall weight of the headphones. Premium materials like memory-foam cushions, leatherette/velour pads, and adjustable headbands improve comfort and also increase durability. Build quality is also important, as better materials and construction naturally increase cost but result in a longer-lasting, more comfortable product. For most people, memory-foam cushions or high-quality leather earpads provide the best balance of comfort and support.
7. Check Battery Life & Charging Features If Wireless Is Your Priority
Battery life is one of the most important factors especially if you travel, work long hours, or listen all day long. Look for models that offer at least 25-40 hours of battery life on a single charge (and even more for over-ear ANC headphones).
Also check for USB-C fast charging, which can significantly reduce downtime. Many modern headphones and earbuds have fast charging features, which provide hours of playback with just a few minutes of charging.
If you want added convenience, consider models with wireless charging cases or battery health optimization, which helps maintain long-term performance over time.
8. Check Headphone Specifications & Features For Detailed Information
Before you buy, review key technical specifications — such as frequency response, impedance, sensitivity, driver size, and codec support — to understand how headphones will perform. Important features like ANC mode, transparency mode, multi-point Bluetooth, app EQ customization, and microphone quality can greatly impact the overall experience.
Also check the Bluetooth version for better stability, water/sweat resistance ratings (such as IPX4 or IPX5), and whether the headset supports features like wear detection, gaming mode, or low latency audio.
Comparing these details carefully will help you avoid surprises and ensure that the product matches your listening style and everyday needs.
9. Confirm Brand Reliability & After-Sales Support
It’s important to consider brand reputation and after-sales support, as these can make a big difference in your long-term satisfaction. Established brands with a track record of quality invest more in consistent build quality, sound performance, and customer service, so you’re less likely to receive a faulty unit or experience issues like early failure.
Check customer reviews, professional audio site ratings, and user feedback to see how a brand performs in real-world use—especially comfort, durability, and how well features like ANC or wireless connectivity hold up over time.
After-sales support is equally important: Look for a warranty, easy repair/replacement policy, and responsive customer service. A good warranty (often 1-2 years) gives you peace of mind, and brands with strong customer support can more smoothly resolve issues like driver failures, connection errors, or battery degradation.
In short, choosing a reliable brand with solid support helps ensure that you not only enjoy great sound right away but also get help if something goes wrong—so you’re not stuck with a headset you can’t use or fix.
10. Budget & Overall Value
Identify your price range and then compare models within that range based on the features you care about most—such as ANC, wireless connectivity, driver type, headset fit, or battery life. Look for product reviews and comparisons to see whether a model offers good performance, long-term comfort, reliable build quality, and strong after-sales support for its price. Sometimes a slightly more expensive pair will pay off in longevity, better sound, and user satisfaction, whereas very cheap models may underperform in isolation, comfort, or consistency.
Ultimately, the goal is to find a headphone that gives you the best combination of features and performance for your budget, rather than overpaying for unused features or settling for inferior sound quality just because a product is cheap.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Once you’ve found and purchased your ideal headphones, proper maintenance plays a key role in extending their lifespan while preserving sound quality and long-term comfort.
Regularly clean the earcups, earpads, and ear tips using a soft, dry cloth or a mild alcohol wipe to remove dirt, sweat, and oil buildup—especially after workouts or extended listening sessions.
If you need to clean your headset, watch this YouTube tutorial video for better understanding:
When not in use, store your headphones in a protective case or place them on a headphone stand, avoid tightly bending or pulling cables, and keep them away from extreme heat, humidity, and dust.

For wireless headphones, charge them responsibly to protect long-term battery health—avoid frequent overcharging or completely draining the battery whenever possible. With proper care, a good pair of headphones can deliver consistent performance and comfort for years to come.
Conclusion:
In this 37+ different types of headphones and earphones guide, we’ve explored nearly every major category—covering fitting styles, enclosure designs, connection types, driver technologies, professional use cases, and real-world listening needs.
From casual earbuds to audiophile-grade headphones and specialized professional headsets, each type serves a specific purpose. Understanding these differences helps you make smarter choices based on comfort, sound quality, features, and budget.
Whether you’re a traveler, gamer, music lover, or professional, choosing the right headphones can significantly enhance your listening experience.
With the knowledge from this guide, you’re now well-equipped to select a pair that truly matches your needs and delivers lasting value.
So, which type of headphones fits your needs best, and which models have you already tried?
Let us know by commenting below! I’ll be happy to hear your thoughts.